An Apriori Algorithm-Based Association Analysis of Analgesic Drugs in Chinese Medicine Prescriptions Recorded From Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis Pain
- PMID: 35959238
- PMCID: PMC9358686
- DOI: 10.3389/fpain.2022.937259
An Apriori Algorithm-Based Association Analysis of Analgesic Drugs in Chinese Medicine Prescriptions Recorded From Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis Pain
Abstract
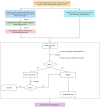
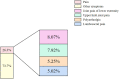
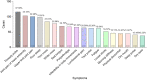
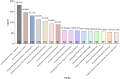
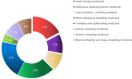
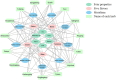
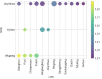
Chronic pain, a common symptom of people with rheumatoid arthritis, usually behaves as persistent polyarthralgia pain and causes serious damage to patients' physical and mental health. Opioid analgesics can lead to a series of side effects like drug tolerance and addiction. Thus, seeking an alternative therapy and screening out the corresponding analgesic drugs is the key to solving the current dilemma. Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) therapy has been recognized internationally for its unique guiding theory and definite curative effect. In this study, we used the Apriori Algorithm to screen out potential analgesics from 311 cases that were treated with compounded medication prescription and collected from "Second Affiliated Hospital of Zhejiang Chinese Medical University" in Hangzhou, China. Data on 18 kinds of clinical symptoms and 16 kinds of Chinese herbs were extracted based on this data mining. We also found 17 association rules and screened out four potential analgesic drugs-"Jinyinhua," "Wugong," "Yiyiren," and "Qingfengteng," which were promised to help in the clinical treatment. Besides, combined with System Cluster Analysis, we provided several different herbal combinations for clinical references.
Keywords: Apriori Algorithm; analgesic drugs; chronic pain; data mining; rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
Copyright © 2022 Lai, Li, Yu, Huang, Zheng, Jiang, Wang, Wen, Chen, Wen and Jin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
[Effect of Tripterygium Glycosides Tablets on immune-induced liver and kidney function in patients with rheumatoid arthritis based on data mining].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2019 Aug;44(16):3526-3532. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20180927.002. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2019. PMID: 31602918 Chinese.
-
[Famous veteran traditional Chinese medicine doctors' medication rules in treating spermatorrhea].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2019 Mar;44(6):1266-1272. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20181128.002. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2019. PMID: 30989993 Chinese.
-
[Prescription and medication regularity of traditional Chinese medicine for treating child pneumonia based on data mining].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2020 Apr;45(8):1942-1947. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20190902.501. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 32489081 Chinese.
-
[Systematic review and screening of basic Chinese herbs for traditional Chinese medicine compounds combined with levodopa medicine in treatment of Parkinson's disease].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2020 Dec;45(24):6043-6052. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20200717.501. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 33496146 Chinese.
-
The treatment of rheumatoid arthritis using Chinese medicinal plants: From pharmacology to potential molecular mechanisms.J Ethnopharmacol. 2015 Dec 24;176:177-206. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2015.10.010. Epub 2015 Oct 22. J Ethnopharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26471289 Review.
Cited by
-
Advantages of Chinese herbal medicine in treating rheumatoid arthritis: a focus on its anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidative effects.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 Mar 7;11:1371461. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1371461. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38515982 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sinomenine regulates immune cell subsets: Potential neuro-immune intervene for precise treatment of chronic pain.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Dec 22;10:1041006. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.1041006. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 36619869 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association between traditional Chinese Medicine and osteoarthritis outcome: A 5-year matched cohort study.Heliyon. 2024 Feb 12;10(4):e26289. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e26289. eCollection 2024 Feb 29. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38390046 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

