Porphyromonas gingivalis: A key role in Parkinson's disease with cognitive impairment?
- PMID: 35959396
- PMCID: PMC9363011
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2022.945523
Porphyromonas gingivalis: A key role in Parkinson's disease with cognitive impairment?
Abstract
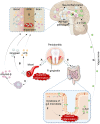
Cognitive impairment (CI) is a common complication of Parkinson's disease (PD). The major features of Parkinson's disease with cognitive impairment (PD-CI) include convergence of α-Synuclein (α-Syn) and Alzheimer's disease (AD)-like pathologies, neuroinflammation, and dysbiosis of gut microbiota. Porphyromonas gingivalis (P. gingivalis) is an important pathogen in periodontitis. Recent research has suggested a role of P. gingivalis and its virulence factor in the pathogenesis of PD and AD, in particular concerning neuroinflammation and deposition of α-Synuclein (α-Syn) and amyloid-β (Aβ). Furthermore, in animal models, oral P. gingivalis could cause neurodegeneration through regulating the gut-brain axis, suggesting an oral-gut-brain axis might exist. In this article, we discussed the pathological characteristics of PD-CI and the role of P. gingivalis in them.
Keywords: Parkinson's disease; Porphyromonas gingivalis; amyloid-β; cognitive impairment; gut microbiota; neuroinflammation; α-Synuclein.
Copyright © 2022 Li, Ren, Li, Liao and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

