Covert vascular brain injury in chronic kidney disease
- PMID: 35959397
- PMCID: PMC9358355
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2022.824503
Covert vascular brain injury in chronic kidney disease
Abstract
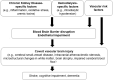
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) contributes to the increased risk of stroke and dementia. Accumulating evidence indicates that structural brain abnormalities, such as cerebral small vessel disease, including white matter hyperintensities, lacunes, perivascular spaces, and cerebral microbleeds, as well as brain atrophy, are common in patients with CKD. All of these imaging findings have been implicated in the development of stroke and dementia. The brain and kidney exhibit similar impairments and promote structural brain abnormalities due to shared vascular risk factors and similar anatomical and physiological susceptibility to vascular injury in patients with CKD. This indicates that kidney function has a significant effect on brain aging. However, as most results are derived from cross-sectional observational studies, the exact pathophysiology of structural brain abnormalities in CKD remains unclear. The early detection of structural brain abnormalities in CKD in the asymptomatic or subclinical phase (covert) should enable stroke risk prediction and guide clinicians on more targeted interventions to prevent stroke in patients with CKD. This article summarizes the currently available clinical evidence linking covert vascular brain injuries with CKD.
Keywords: albuminuria; brain; cerebral small vessel diseases; chronic kidney disease; stroke.
Copyright © 2022 Miwa and Toyoda.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources