Protein Kinase A in cellular migration-Niche signaling of a ubiquitous kinase
- PMID: 35959460
- PMCID: PMC9361040
- DOI: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.953093
Protein Kinase A in cellular migration-Niche signaling of a ubiquitous kinase
Abstract
Cell migration requires establishment and maintenance of directional polarity, which in turn requires spatial heterogeneity in the regulation of protrusion, retraction, and adhesion. Thus, the signaling proteins that regulate these various structural processes must also be distinctly regulated in subcellular space. Protein Kinase A (PKA) is a ubiquitous serine/threonine kinase involved in innumerable cellular processes. In the context of cell migration, it has a paradoxical role in that global inhibition or activation of PKA inhibits migration. It follows, then, that the subcellular regulation of PKA is key to bringing its proper permissive and restrictive functions to the correct parts of the cell. Proper subcellular regulation of PKA controls not only when and where it is active but also specifies the targets for that activity, allowing the cell to use a single, promiscuous kinase to exert distinct functions within different subcellular niches to facilitate cell movement. In this way, understanding PKA signaling in migration is a study in context and in the elegant coordination of distinct functions of a single protein in a complex cellular process.
Keywords: Rho GTPases; cell migration; compartmentalization; ion channels; leading edge; protein kinase A; subcellular signaling; tyrosine kinases.
Copyright © 2022 Svec and Howe.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
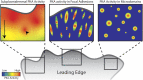
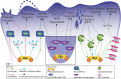
References
-
- Adame-García S. R., Cervantes-Villagrana R. D., Orduña-Castillo L. B., Del Rio J. C., Gutkind J. S., Reyes-Cruz G., et al. (2019). cAMP-dependent activation of the Rac guanine exchange factor P-REX1 by type I protein kinase A (PKA) regulatory subunits. J. Biol. Chem. 294 (7), 2232–2246. 10.1074/jbc.RA118.006691 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

