Epigenetic modification mechanism of histone demethylase KDM1A in regulating cardiomyocyte apoptosis after myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury
- PMID: 35959481
- PMCID: PMC9359132
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.13823
Epigenetic modification mechanism of histone demethylase KDM1A in regulating cardiomyocyte apoptosis after myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury
Abstract
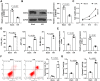
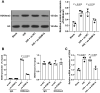
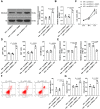
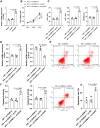
Hypoxia and reoxygenation (H/R) play a prevalent role in heart-related diseases. Histone demethylases are involved in myocardial injury. In this study, the mechanism of the lysine-specific histone demethylase 1A (KDM1A/LSD1) on cardiomyocyte apoptosis after myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury (MIRI) was investigated. Firstly, HL-1 cells were treated with H/R to establish the MIRI models. The expressions of KDM1A and Sex Determining Region Y-Box Transcription Factor 9 (SOX9) in H/R-treated HL-1 cells were examined. The cell viability, markers of myocardial injury (LDH, AST, and CK-MB) and apoptosis (Bax and Bcl-2), and Caspase-3 and Caspase-9 protein activities were detected, respectively. We found that H/R treatment promoted cardiomyocyte apoptosis and downregulated KDM1A, and overexpressing KDM1A reduced apoptosis in H/R-treated cardiomyocytes. Subsequently, tri-methylation of lysine 4 on histone H3 (H3K4me3) level on the SOX9 promoter region was detected. We found that KDM1A repressed SOX9 transcription by reducing H3K4me3. Then, HL-1 cells were treated with CPI-455 and plasmid pcDNA3.1-SOX9 and had joint experiments with pcDNA3.1-KDM1A. We disclosed that upregulating H3K4me3 or overexpressing SOX9 reversed the inhibitory effect of overexpressing KDM1A on apoptosis of H/R-treated cardiomyocytes. In conclusion, KDM1A inhibited SOX9 transcription by reducing the H3K4me3 on the SOX9 promoter region and thus inhibited H/R-induced apoptosis of cardiomyocytes.
Keywords: Bax; Bcl-2; Cardiomyocyte apoptosis; H3K4me3; Histone demethylation; Hypoxia-reoxygenation; KDM1A; SOX9.
©2022 He et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there are no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Chen Z, Guo W, Wu Q, Tan L, Ma T, Fu C, Yu J, Ren X, Wang J, Liang P, Meng X. Tumor reoxygenation for enhanced combination of radiation therapy and microwave thermal therapy using oxygen generation in situ by CuO nanosuperparticles under microwave irradiation. Theranostics. 2020;10(10):4659–4675. doi: 10.7150/thno.42818. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

