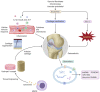
Exosomes in osteoarthritis: Updated insights on pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment
- PMID: 35959489
- PMCID: PMC9362859
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2022.949690
Exosomes in osteoarthritis: Updated insights on pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment
Abstract
Osteoarthritis (OA) has remained a prevalent public health problem worldwide over the past decades. OA is a global challenge because its specific pathogenesis is unclear, and no effective disease-modifying drugs are currently available. Exosomes are small and single-membrane vesicles secreted via the formation of endocytic vesicles and multivesicular bodies (MVBs), which are eventually released when MVBs fuse with the plasma membrane. Exosomes contain various integral surface proteins derived from cells, intercellular proteins, DNAs, RNAs, amino acids, and metabolites. By transferring complex constituents and promoting macrophages to generate chemokines and proinflammatory cytokines, exosomes function in pathophysiological processes in OA, including local inflammation, cartilage calcification and degradation of osteoarthritic joints. Exosomes are also detected in synovial fluid and plasma, and their levels continuously change with OA progression. Thus, exosomes, specifically exosomal miRNAs and lncRNAs, potentially represent multicomponent diagnostic biomarkers for OA. Exosomes derived from various types of mesenchymal stem cells and other cell or tissue types affect angiogenesis, inflammation, and bone remodeling. These exosomes exhibit promising capabilities to restore OA cartilage, attenuate inflammation, and balance cartilage matrix formation and degradation, thus demonstrating therapeutic potential in OA. In combination with biocompatible and highly adhesive materials, such as hydrogels and cryogels, exosomes may facilitate cartilage tissue engineering therapies for OA. Based on numerous recent studies, we summarized the latent mechanisms and clinical value of exosomes in OA in this review.
Keywords: biomarkers; cartilage; cartilage tissue engineering; exosomes; osteoarthritis.
Copyright © 2022 Fan, Liu, Pan, Wang, Ding, Zhang, Ye, Zhou, An and Xiao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Exosomes in Osteoarthritis: A Review on Their Isolation Techniques and Therapeutic Potential.Indian J Orthop. 2024 May 21;58(7):866-875. doi: 10.1007/s43465-024-01175-7. eCollection 2024 Jul. Indian J Orthop. 2024. PMID: 38948378 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosomes in osteoarthritis and cartilage injury: advanced development and potential therapeutic strategies.Int J Biol Sci. 2020 Mar 31;16(11):1811-1820. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.41637. eCollection 2020. Int J Biol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32398951 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosomes in the Pathogenesis, Progression, and Treatment of Osteoarthritis.Bioengineering (Basel). 2022 Feb 27;9(3):99. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering9030099. Bioengineering (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35324788 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Osteoarthritic Subchondral Bone Release Exosomes That Promote Cartilage Degeneration.Cells. 2021 Jan 28;10(2):251. doi: 10.3390/cells10020251. Cells. 2021. PMID: 33525381 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular vesicles: Potential role in osteoarthritis regenerative medicine.J Orthop Translat. 2019 Dec 6;21:73-80. doi: 10.1016/j.jot.2019.10.012. eCollection 2020 Mar. J Orthop Translat. 2019. PMID: 32099807 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Advances in the Study of Exosomes as Drug Delivery Systems for Bone-Related Diseases.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Jan 9;15(1):220. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15010220. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 36678850 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current Knowledge and Future Perspectives of Exosomes as Nanocarriers in Diagnosis and Treatment of Diseases.Int J Nanomedicine. 2023 Aug 21;18:4751-4778. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S417422. eCollection 2023. Int J Nanomedicine. 2023. PMID: 37635911 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of microRNA carried by small extracellular vesicles in urological tumors.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Jun 2;11:1192937. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1192937. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 37333986 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stem Cell Exosomes for Osteoarthritis in Veterinary Medicine.Stem Cells Int. 2025 Jul 16;2025:4888569. doi: 10.1155/sci/4888569. eCollection 2025. Stem Cells Int. 2025. PMID: 40704321 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Controlled Stimulus-Responsive Delivery Systems for Osteoarthritis Treatment.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Nov 2;25(21):11799. doi: 10.3390/ijms252111799. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39519350 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous