Phenotypic expansion of ARSK-related mucopolysaccharidosis
- PMID: 35959767
- PMCID: PMC9804171
- DOI: 10.1002/ajmg.a.62934
Phenotypic expansion of ARSK-related mucopolysaccharidosis
Keywords: ARSK; arylsulfatase K; mucopolysaccharidosis; skeletal.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
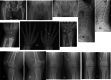
Figures
References
-
- Barker, D. , & Welbury, R. R. (2000). Dental findings in Morquio syndrome (mucopolysaccharidosis type Iva). ASDC Journal of Dentistry for Children, 67(6), 431–433. - PubMed
-
- Mendelsohn, N. J. , Wood, T. , Olson, R. A. , Temme, R. , Hale, S. , Zhang, H. , Read, L. , & White, K. K. (2013). Spondyloepiphyseal dysplasias and bilateral legg‐calvé‐perthes disease: Diagnostic considerations for mucopolysaccharidoses. JIMD Reports, 11, 125–132. 10.1007/8904_2013_231 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ribeiro, E. M. , Fonteles, C. S. , Freitas, A. B. , da Silva Alves, K. S. , Monteiro, A. J. , & da Silva, C. A. (2015). A clinical multicenter study of orofacial features in 26 brazilian patinets with different types of mucoploysaccharidosis. The Cleft palate‐Craniofacial Journal, 52, 352–358. 10.1597/13-204 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Verheyen, S. , Blatterer, J. , Speicher, M. R. , Bhavani, G. S. L. , Boons, G. J. , Ilse, M. B. , Andrae, D. , Sproß, J. , Vaz, F. M. , Kircher, S. G. , Posch‐Pertl, L. , Baumgartner, D. , Lübke, T. , Shah, H. , al Kaissi, A. , Girisha, K. M. , & Plecko, B. (2021). Novel subtype of mucopolysaccharidosis caused by arylsulfatase K (ARSK) deficiency. Journal of Medical Genetics, 1‐8. 10.1136/jmedgenet-2021-108061 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

