Inflammatory stress signaling via NF- k B alters accessible cholesterol to upregulate SREBP2 transcriptional activity in endothelial cells
- PMID: 35959888
- PMCID: PMC9395194
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.79529
Inflammatory stress signaling via NF- k B alters accessible cholesterol to upregulate SREBP2 transcriptional activity in endothelial cells
Abstract
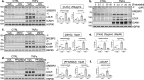
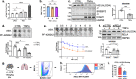
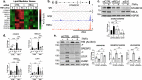
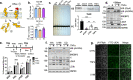
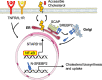
There is a growing appreciation that a tight relationship exists between cholesterol homeostasis and immunity in leukocytes; however, this relationship has not been deeply explored in the vascular endothelium. Endothelial cells (ECs) rapidly respond to extrinsic signals, such as tissue damage or microbial infection, by upregulating factors to activate and recruit circulating leukocytes to the site of injury and aberrant activation of ECs leads to inflammatory based diseases, such as multiple sclerosis and atherosclerosis. Here, we studied the role of cholesterol and a key transcription regulator of cholesterol homeostasis, SREBP2, in the EC responses to inflammatory stress. Treatment of primary human ECs with pro-inflammatory cytokines upregulated SREBP2 cleavage and cholesterol biosynthetic gene expression within the late phase of the acute inflammatory response. Furthermore, SREBP2 activation was dependent on NF-κB DNA binding and canonical SCAP-SREBP2 processing. Mechanistically, inflammatory activation of SREBP was mediated by a reduction in accessible cholesterol, leading to heightened sterol sensing and downstream SREBP2 cleavage. Detailed analysis of NF-κB inducible genes that may impact sterol sensing resulted in the identification of a novel RELA-inducible target, STARD10, that mediates accessible cholesterol homeostasis in ECs. Thus, this study provides an in-depth characterization of the relationship between cholesterol homeostasis and the acute inflammatory response in EC.
Keywords: ALOD4; SREBP2; cholesterol; endothelial; human; immunology; inflammation.
© 2022, Fowler et al.
Conflict of interest statement
JF, RZ, BT, NB, WS No competing interests declared
Figures





Similar articles
-
SREBP2 regulates the endothelial response to cytokines via direct transcriptional activation of KLF6.J Lipid Res. 2023 Aug;64(8):100411. doi: 10.1016/j.jlr.2023.100411. Epub 2023 Jul 10. J Lipid Res. 2023. PMID: 37437844 Free PMC article.
-
Epithelial Cholesterol Deficiency Attenuates Human Antigen R-linked Pro-inflammatory Stimulation via an SREBP2-linked Circuit.J Biol Chem. 2016 Nov 18;291(47):24641-24656. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.723973. Epub 2016 Oct 4. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27703009 Free PMC article.
-
Sterol-responsive element-binding protein (SREBP) 2 down-regulates ATP-binding cassette transporter A1 in vascular endothelial cells: a novel role of SREBP in regulating cholesterol metabolism.J Biol Chem. 2004 Nov 19;279(47):48801-7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M407817200. Epub 2004 Sep 8. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15358760
-
Endothelial dysfunction: the role of sterol regulatory element-binding protein-induced NOD-like receptor family pyrin domain-containing protein 3 inflammasome in atherosclerosis.Curr Opin Lipidol. 2014 Oct;25(5):339-49. doi: 10.1097/MOL.0000000000000107. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2014. PMID: 25188917 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Maintaining cholesterol homeostasis: sterol regulatory element-binding proteins.World J Gastroenterol. 2004 Nov 1;10(21):3081-7. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i21.3081. World J Gastroenterol. 2004. PMID: 15457548 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
TNFα Activates the Liver X Receptor Signaling Pathway and Promotes Cholesterol Efflux from Human Brain Pericytes Independently of ABCA1.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 22;24(6):5992. doi: 10.3390/ijms24065992. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36983062 Free PMC article.
-
The crosstalk between neuropilin-1 and tumor necrosis factor-α in endothelial cells.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Jun 27;12:1210944. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1210944. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 38994453 Free PMC article.
-
The dynamic equilibrium between the protective and toxic effects of matrine in the development of liver injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jan 29;15:1315584. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1315584. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38348397 Free PMC article.
-
TNFα increases the degradation of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 4 by the Lon protease to support proinflammatory genes.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023 Sep 19;120(38):e2218150120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2218150120. Epub 2023 Sep 11. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023. PMID: 37695914 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear SREBP2 condensates regulate the transcriptional activation of lipogenic genes and cholesterol homeostasis.Nat Metab. 2025 May;7(5):1034-1051. doi: 10.1038/s42255-025-01291-0. Epub 2025 May 20. Nat Metab. 2025. PMID: 40394324
References
-
- Abrams ME, Johnson KA, Perelman SS, Zhang LS, Endapally S, Mar KB, Thompson BM, McDonald JG, Schoggins JW, Radhakrishnan A, Alto NM. Oxysterols provide innate immunity to bacterial infection by mobilizing cell surface accessible cholesterol. Nature Microbiology. 2020;5:929–942. doi: 10.1038/s41564-020-0701-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Araldi E, Fernández-Fuertes M, Canfrán-Duque A, Tang W, Cline GW, Madrigal-Matute J, Pober JS, Lasunción MA, Wu D, Fernández-Hernando C, Suárez Y. Lanosterol modulates TLR4-mediated innate immune responses in macrophages. Cell Reports. 2017;19:2743–2755. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.05.093. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bekkering S, Arts RJW, Novakovic B, Kourtzelis I, van der Heijden CDCC, Li Y, Popa CD, Ter Horst R, van Tuijl J, Netea-Maier RT, van de Veerdonk FL, Chavakis T, Joosten LAB, van der Meer JWM, Stunnenberg H, Riksen NP, Netea MG. Metabolic induction of trained immunity through the mevalonate pathway. Cell. 2018;172:135–146. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.11.025. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

