Plasma exchange in the intensive care unit: a narrative review
- PMID: 35960275
- PMCID: PMC9372988
- DOI: 10.1007/s00134-022-06793-z
Plasma exchange in the intensive care unit: a narrative review
Abstract
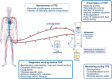
In this narrative review, we discuss the relevant issues of therapeutic plasma exchange (TPE) in critically ill patients. For many conditions, the optimal indication, device type, frequency, duration, type of replacement fluid and criteria for stopping TPE are uncertain. TPE is a potentially lifesaving but also invasive procedure with risk of adverse events and complications and requires close monitoring by experienced teams. In the intensive care unit (ICU), the indications for TPE can be divided into (1) absolute, well-established, and evidence-based, for which TPE is recognized as first-line therapy, (2) relative, for which TPE is a recognized second-line treatment (alone or combined) and (3) rescue therapy, where TPE is used with a limited or theoretical evidence base. New indications are emerging and ongoing knowledge gaps, notably regarding the use of TPE during critical illness, support the establishment of a TPE registry dedicated to intensive care medicine.
Keywords: Intensive care units; Patient care team; Plasma exchange; Plasmapheresis; State-of-the-art review.
© 2022. Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
JC received speaker fees from Fresenius Kabi and Terumo Blood and Cell Technologies. JTK received speaker fees from Fresenius Medical Care and ExThera Medical.
Figures
References
-
- Padmanabhan A, Connelly-Smith L, Aqui N, Balogun RA, Klingel R, Meyer E, Pham HP, Schneiderman J, Witt V, Wu Y, Zantek ND, Dunbar NM, Schwartz GEJ. Guidelines on the use of therapeutic apheresis in clinical practice—evidence-based approach from the Writing Committee of the American Society for Apheresis: the eighth special issue. J Clin Apher. 2019;34:171–354. doi: 10.1002/jca.21705. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Abe T, Matsuo H, Abe R, Abe S, Asada H, Ashida A, Baba A, Eguchi K, Eguchi Y, Endo Y, Fujimori Y, Furuichi K, Furukawa Y, Furuya M, Furuya T, Hanafusa N, Hara W, Harada-Shiba M, Hasegawa M, Hattori N, Hattori M, Hidaka S, Hidaka T, Hirayama C, Ikeda S, Imamura H, Inoue K, Ishizuka K, Ishizuka K, Ito T, Iwamoto H, Izaki S, Kagitani M, Kaneko S, Kaneko N, Kanekura T, Kitagawa K, Kusaoi M, Lin Y, Maeda T, Makino H, Makino S, Matsuda K, Matsugane T, Minematsu Y, Mineshima M, Miura K, Miyamoto K, Moriguchi T, Murata M, Naganuma M, Nakae H, Narukawa S, Nohara A, Nomura K, Ochi H, Ohkubo A, Ohtake T, Okada K, Okado T, Okuyama Y, Omokawa S, Oji S, Sakai N, Sakamoto Y, Sasaki S, Sato M, Seishima M, Shiga H, Shimohata H, Sugawara N, Sugimoto K, Suzuki Y, Suzuki M, Tajima T, Takikawa Y, Tanaka S, Taniguchi K, Tsuchida S, Tsukamoto T, Tsushima K, Ueda Y, Wada T, Yamada H, Yamada H, Yamaka T, Yamamoto K, Yokoyama Y, Yoshida N, Yoshioka T, Yamaji K. The Japanese Society for Apheresis clinical practice guideline for therapeutic apheresis. Ther Apher Dial. 2021;25:728–876. doi: 10.1111/1744-9987.13749. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources