A Novel Dual-Energy CT Method for Detection and Differentiation of Intracerebral Hemorrhage From Contrast Extravasation in Stroke Patients After Endovascular Thrombectomy : Feasibility and First Results
- PMID: 35960327
- PMCID: PMC10014653
- DOI: 10.1007/s00062-022-01198-3
A Novel Dual-Energy CT Method for Detection and Differentiation of Intracerebral Hemorrhage From Contrast Extravasation in Stroke Patients After Endovascular Thrombectomy : Feasibility and First Results
Abstract
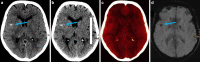
Purpose: Dual-energy computed tomography (DECT) has been shown to be able to differentiate between intracranial hemorrhage (ICH) and extravasation of iodinated contrast media (contrast staining [CS]). TwinSpiral DECT is a recently introduced technique, which allows image acquisition at two different energy levels in two consecutive spiral scans. The aim of this study was to evaluate the feasibility and accuracy of TwinSpiral DECT to distinguish between ICH and CS after endovascular thrombectomy (EVT) in patients with acute ischemic stroke.
Methods: This retrospective single-center study conducted between November 2019 and July 2020 included non-contrast TwinSpiral DECT scans (tube voltages 80 and 150Sn kVp) of 39 ischemic stroke patients (18 females, 21 males, mean age 69 ± 11 years) within 48-72 h after endovascular thrombectomy. Parenchymal hyperdensity was assessed for the presence of ICH or/and CS by two board certified and fellowship-trained, blinded and independent neuroradiologists using standard mixed images and virtual non-contrast (VNC) images with corresponding iodine maps from TwinSpiral DECT. Follow-up examinations (FU; CT or MRI) were used as a standard of reference. Sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy for the detection of ICH as well as the inter-reader agreement were calculated.
Results: Parenchymal hyperdensities were detected in 17/39 (44%) patients. Using DECT, they were classified by both readers as ICH in 9 (53%), CS in 8 (47%), and mixture of both in 6 (35%) cases with excellent agreement (κ = 0.81, P < 0.0001). The sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy for the detection of ICH in DECT was 90% (95% confidence interval [CI]: 84-96%), 100% (95% CI 94-100%) and 95% (95% CI 89-100%), and in mixed images 90% (95% CI 84-96%), 86% (95% CI 80-92%) and 88% (95% CI 82-94%), respectively. Inter-reader agreement for detecting ICH on DECT compared to the mixed images was κ = 1.00 (P < 0.0001) vs. κ = 0.51 (P = 0.034).
Conclusion: TwinSpiral DECT demonstrates high accuracy and excellent specificity for differentiating ICH from CS in patients after mechanical thrombectomy due to acute ischemic stroke, and improves inter-reader agreement for detecting ICH compared to the standard mixed images.
Keywords: Brain hemorrhage; Cerebrovascular accident; Contrast extravasation; Endovascular treatment; Spectral computed tomography.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
R. Grkovski, L. Acu, U. Ahmadli, R. Terziev, T. Schubert, S. Wegener, Z. Kulcsár, S. Husain, H. Alkadhi and S. Winklhofer declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Dual-Energy Computed Tomography in Stroke Imaging : Value of a New Image Acquisition Technique for Ischemia Detection after Mechanical Thrombectomy.Clin Neuroradiol. 2023 Sep;33(3):747-754. doi: 10.1007/s00062-023-01270-6. Epub 2023 Mar 2. Clin Neuroradiol. 2023. PMID: 36862231 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic accuracy of dual-energy computed tomography to differentiate intracerebral hemorrhage from contrast extravasation after endovascular thrombectomy for acute ischemic stroke: systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur Radiol. 2022 Jan;32(1):432-441. doi: 10.1007/s00330-021-08212-1. Epub 2021 Jul 29. Eur Radiol. 2022. PMID: 34327578
-
Early diagnosis and prediction of intracranial hemorrhage using dual-energy computed tomography after mechanical thrombectomy in patients with acute ischemic stroke.Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2021 Apr;203:106551. doi: 10.1016/j.clineuro.2021.106551. Epub 2021 Feb 10. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2021. PMID: 33636506
-
Iodine Extravasation Quantification on Dual-Energy CT of the Brain Performed after Mechanical Thrombectomy for Acute Ischemic Stroke Can Predict Hemorrhagic Complications.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2018 Mar;39(3):441-447. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A5513. Epub 2018 Jan 18. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2018. PMID: 29348131 Free PMC article.
-
Dual-energy CT for differentiating acute intracranial hemorrhage from contrast staining or calcification: a meta-analysis.Neuroradiology. 2020 Dec;62(12):1617-1626. doi: 10.1007/s00234-020-02486-w. Epub 2020 Jul 4. Neuroradiology. 2020. PMID: 32621024
Cited by
-
Quantification of ischemic brain edema after mechanical thrombectomy using dual-energy computed tomography in patients with ischemic stroke.Sci Rep. 2024 Feb 20;14(1):4148. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-54600-0. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38378795 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative contrast enhancement volume on immediate post-thrombectomy CT predicts symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage and functional outcomes in acute large vessel occlusion stroke.Front Neurol. 2025 May 29;16:1579659. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1579659. eCollection 2025. Front Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40510208 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic accuracy of dual-energy computed tomography in the diagnosis of neurological complications after endovascular treatment of acute ischaemic stroke: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Br J Radiol. 2024 Jan 23;97(1153):73-92. doi: 10.1093/bjr/tqad007. Br J Radiol. 2024. PMID: 38263833 Free PMC article.
-
Mobile photon counting detector CT with multi material decomposition methods for neuroimaging of patients in intensive care unit.Sci Rep. 2024 Dec 30;14(1):31745. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-81735-x. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39738332 Free PMC article.
-
Dual-Energy Computed Tomography in Stroke Imaging : Value of a New Image Acquisition Technique for Ischemia Detection after Mechanical Thrombectomy.Clin Neuroradiol. 2023 Sep;33(3):747-754. doi: 10.1007/s00062-023-01270-6. Epub 2023 Mar 2. Clin Neuroradiol. 2023. PMID: 36862231 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Renú A, Laredo C, Rodríguez-Vázquez A, Santana D, Werner M, Llull L, Lopez-Rueda A, Urra X, Rudilosso S, Obach V, Amaro S, Chamorro Á. Characterization of Subarachnoid Hyperdensities After Thrombectomy for Acute Stroke Using Dual-Energy CT. Neurology. 2022;98:e601–e611. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000013198. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Winklhofer S, De Martini VI, Nern C, Blume I, Wegener S, Pangalu A, Valavanis A, Alkadhi H, Guggenberger R. Dual-Energy Computed Tomography in Stroke Imaging: Technical and Clinical Considerations of Virtual Noncontrast Images for Detection of the Hyperdense Artery Sign. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2017;41:843–848. doi: 10.1097/RCT.0000000000000638. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Siegel MJ, Kaza RK, Bolus DN, Boll DT, Rofsky NM, De Cecco CN, Foley WD, Morgan DE, Schoepf UJ, Sahani DV, Shuman WP, Vrtiska TJ, Yeh BM, Berland LL. White Paper of the Society of Computed Body Tomography and Magnetic Resonance on Dual-Energy CT, Part 1: Technology and Terminology. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2016;40:841–845. doi: 10.1097/RCT.0000000000000531. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

