miR-22 alleviates sepsis-induced acute kidney injury via targeting the HMGB1/TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway
- PMID: 35960478
- PMCID: PMC9859886
- DOI: 10.1007/s11255-022-03321-2
miR-22 alleviates sepsis-induced acute kidney injury via targeting the HMGB1/TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway
Abstract
Background: Acute kidney injury (AKI) is a severe complication of sepsis, and is strongly correlated with MicroRNAs (miRNAs). However, the mechanism of miR-22 on sepsis-induced AKI is not clearly understood. The study aimed to explore the role and mechanism of miR-22 on AKI.
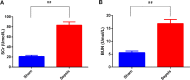
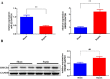
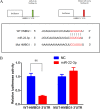
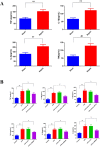
Methods: The AKI models were established by cecal ligation and puncture (CLP) surgery in SD rats and lipopolysaccharide (LPS) induction in HBZY-1 cells. In AKI rats, the content of serum creatinine (SCr) and blood urea nitrogen (BUN) were detected. Kidney tissues were pathologically examined by H&E and PAS staining. The LPS-induced HBZY-1 cells were transfected with mimics miR-22, si-HMGB1, or oe-HMGB1. miR-22 and HMGB1 expression was detected in vivo and in vitro. In transfected cells, HMGB1/TLR4/NF-κB pathway-related protein expressions were measured by Western blot. The relationship between miR-22 and HMGB1 was assessed by a dual-luciferase gene report. Inflammatory cytokine levels in serum and cells were assessed by ELISA.
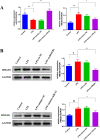
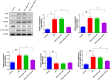
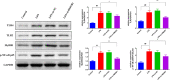
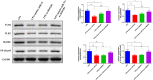
Results: In AKI rats, kidney injury was observed, accompanied by the down-regulated miR-122 expression and up-regulated HMBG1 expression. The dual-luciferase report found miR-22-3p could targetly regulate HMBG1. Furthermore, both in vitro and in vivo experiments revealed that the releases of inflammatory cytokine were increased after AKI modeling, but the situation was reversed by mimics miR-22 or si-HMGB1 in vitro. In HBZY-1 cells, mimics miR-22 could suppress LPS-induced overexpression of HMGB1/TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway-related proteins. However, the oe-HMGB1 addition reversed the effect of mimics miR-22.
Conclusion: miR-22 can inhibit the inflammatory response, target the HMGB1, and inhibit the HMGB1/TLR4/NF-kB pathway, to attenuate the sepsis-induced AKI, which indicates that miR-22 may serve as a potential treatment target in sepsis-induced AKI.
Keywords: Acute kidney injury; HMGB1; Sepsis; Signaling pathway; microRNA.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Usp9x contributes to the development of sepsis-induced acute kidney injury by promoting inflammation and apoptosis in renal tubular epithelial cells via activation of the TLR4/nf-κb pathway.Ren Fail. 2024 Dec;46(2):2361089. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2024.2361089. Epub 2024 Jun 14. Ren Fail. 2024. PMID: 38874156 Free PMC article.
-
miR-129-5p alleviates LPS-induced acute kidney injury via targeting HMGB1/TLRs/NF-kappaB pathway.Int Immunopharmacol. 2020 Dec;89(Pt A):107016. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107016. Epub 2020 Oct 8. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 33039954
-
MicroRNA-23a-3p ameliorates acute kidney injury by targeting FKBP5 and NF-κB signaling in sepsis.Cytokine. 2022 Jul;155:155898. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2022.155898. Epub 2022 May 7. Cytokine. 2022. PMID: 35537329
-
Epigenetic dysregulation of autophagy in sepsis-induced acute kidney injury: the underlying mechanisms for renoprotection.Front Immunol. 2023 May 5;14:1180866. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1180866. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37215112 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Toll-like Receptor 4 in Acute Kidney Injury.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 11;24(2):1415. doi: 10.3390/ijms24021415. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36674930 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Knockdown of circ-Gatad1 alleviates LPS induced HK2 cell injury via targeting miR-22-3p/TRPM7 axis in septic acute kidney.BMC Nephrol. 2024 Mar 5;25(1):79. doi: 10.1186/s12882-024-03513-1. BMC Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 38443846 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical significance of miR-625-5p in patients with sepsis-induced acute kidney injury based on bioinformatics analysis.Int Urol Nephrol. 2025 Feb;57(2):603-611. doi: 10.1007/s11255-024-04209-z. Epub 2024 Sep 19. Int Urol Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 39294516
-
Usp9x contributes to the development of sepsis-induced acute kidney injury by promoting inflammation and apoptosis in renal tubular epithelial cells via activation of the TLR4/nf-κb pathway.Ren Fail. 2024 Dec;46(2):2361089. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2024.2361089. Epub 2024 Jun 14. Ren Fail. 2024. PMID: 38874156 Free PMC article.
-
Unveiling the Therapeutic Potential of Dulaglutide in Mitigating Tacrolimus-Induced Nephrotoxicity Through Targeting the miR-22/HMGB-1/TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB Trajectory.Arch Pharm (Weinheim). 2025 Apr;358(4):e3127. doi: 10.1002/ardp.202500023. Arch Pharm (Weinheim). 2025. PMID: 40205909 Free PMC article.
-
High-mobility group box 1 and its related receptors: potential therapeutic targets for contrast-induced acute kidney injury.Int Urol Nephrol. 2024 Jul;56(7):2291-2299. doi: 10.1007/s11255-024-03981-2. Epub 2024 Mar 5. Int Urol Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 38438703 Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

