Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy Reduces Patient-Reported Chronic Toxicity Compared With Conventional Pelvic Radiation Therapy: Updated Results of a Phase III Trial
- PMID: 35960897
- PMCID: PMC9851703
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.21.02831
Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy Reduces Patient-Reported Chronic Toxicity Compared With Conventional Pelvic Radiation Therapy: Updated Results of a Phase III Trial
Abstract
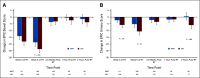
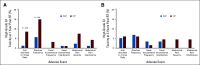
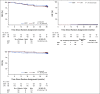
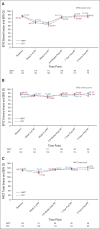
Clinical trials frequently include multiple end points that mature at different times. The initial report, typically based on the primary end point, may be published when key planned coprimary or secondary analyses are not yet available. Clinical Trial Updates provide an opportunity to disseminate additional results from studies, published in JCO or elsewhere, for which the primary end point has already been reported.The purpose of this update was to determine differences in patient-reported chronic toxicity and disease outcomes with intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) compared with conventional pelvic radiation. Patients with cervical and endometrial cancers who received postoperative pelvic radiation were randomly assigned to conventional radiation therapy (CRT) or IMRT. Toxicity and quality of life were assessed using Patient-Reported Outcomes version of the Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events, Expanded Prostate Cancer Index Composite (EPIC) bowel and urinary domains, and Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy-General. Between 2012 and 2015, 279 eligible patients were enrolled to the study with a median follow-up of 37.8 months. There were no differences in overall survival (P = .53), disease-free survival (P = .21), or locoregional failure (P = .81). One year after RT, patients in the CRT arm experienced more high-level diarrhea frequency (5.8% IMRT v 15.1% CRT, P = .042) and a greater number had to take antidiarrheal medication two or more times a day (1.2% IMRT v 8.6% CRT, P = .036). At 3 years, women in the CRT arm reported a decline in urinary function, whereas the IMRT arm continued to improve (mean change in EPIC urinary score = 0.5, standard deviation = 13.0, IMRT v -6.0, standard deviation = 14.3, CRT, P = .005). In conclusion, IMRT reduces patient-reported chronic GI and urinary toxicity with no difference in treatment efficacy at 3 years.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01672892.
Conflict of interest statement
No other potential conflicts of interest were reported.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Patient-Reported Toxicity During Pelvic Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy: NRG Oncology-RTOG 1203.J Clin Oncol. 2018 Aug 20;36(24):2538-2544. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2017.77.4273. Epub 2018 Jul 10. J Clin Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29989857 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
[A randomized study of intensity-modulated radiation therapy versus three dimensional conformal radiation therapy for pelvic radiation in patients of post-operative treatment with gynecologic malignant tumor].Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi. 2017 Mar 25;52(3):168-174. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0529-567X.2017.03.006. Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi. 2017. PMID: 28355688 Clinical Trial. Chinese.
-
Late Toxicity After Adjuvant Conventional Radiation Versus Image-Guided Intensity-Modulated Radiotherapy for Cervical Cancer (PARCER): A Randomized Controlled Trial.J Clin Oncol. 2021 Nov 20;39(33):3682-3692. doi: 10.1200/JCO.20.02530. Epub 2021 Sep 10. J Clin Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34506246 Clinical Trial.
-
Acute toxicity with intensity modulated radiotherapy versus 3-dimensional conformal radiotherapy during preoperative chemoradiation for locally advanced rectal cancer.Radiother Oncol. 2016 Nov;121(2):252-257. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2016.09.010. Epub 2016 Oct 14. Radiother Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27751605 Review.
-
Chronic skin toxicities in breast cancer survivors: a systematic review and meta-analysis of radiotherapy techniques.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2025 Jul;212(1):1-12. doi: 10.1007/s10549-025-07700-y. Epub 2025 May 5. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2025. PMID: 40323361 Review.
Cited by
-
Editorial: Recent advances in cervical cancer radiotherapy.Front Oncol. 2023 Feb 15;13:1144797. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1144797. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36874140 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Impact of reduced margin pelvic radiotherapy on gastrointestinal toxicity and outcome in gynecological cancer.Clin Transl Radiat Oncol. 2023 Aug 28;43:100671. doi: 10.1016/j.ctro.2023.100671. eCollection 2023 Nov. Clin Transl Radiat Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37692995 Free PMC article.
-
Adverse Event Reporting in Cancer Clinical Trials: Incorporating Patient-Reported Methods. A Systematic Scoping Review.Patient. 2024 Jul;17(4):335-347. doi: 10.1007/s40271-024-00689-4. Epub 2024 Apr 8. Patient. 2024. PMID: 38589749 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of PM2.5 exposure on acute toxicities and survival outcomes in radiotherapy for cervical cancer.Sci Rep. 2025 Aug 20;15(1):30557. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-15852-6. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40835997 Free PMC article.
-
Advances and Challenges in Conducting Clinical Trials With Proton Beam Therapy.Semin Radiat Oncol. 2023 Oct;33(4):407-415. doi: 10.1016/j.semradonc.2023.06.006. Semin Radiat Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37684070 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Peters WA III, Liu PY, Barrett RJ II, et al. : Concurrent chemotherapy and pelvic radiation therapy compared with pelvic radiation therapy alone as adjuvant therapy after radical surgery in high-risk early-stage cancer of the cervix. J Clin Oncol 18:1606-1613, 2000 - PubMed
-
- Sedlis A, Bundy BN, Rotman MZ, et al. : A randomized trial of pelvic radiation therapy versus no further therapy in selected patients with stage IB carcinoma of the cervix after radical hysterectomy and pelvic lymphadenectomy: A Gynecologic Oncology Group study. Gynecol Oncol 73:177-183, 1999 - PubMed
-
- Creutzberg CL, Nout RA, Lybeert ML, et al. : Fifteen-year radiotherapy outcomes of the randomized PORTEC-1 trial for endometrial carcinoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 81:e631-8, 2011 - PubMed
-
- Keys HM, Roberts JA, Brunetto VL, et al. : A phase III trial of surgery with or without adjunctive external pelvic radiation therapy in intermediate risk endometrial adenocarcinoma: A Gynecologic Oncology Group study. Gynecol Oncol 92:744-751, 2004 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

