Genomic and transcriptomic profiling of phoenix colonies
- PMID: 35962051
- PMCID: PMC9374717
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-18059-1
Genomic and transcriptomic profiling of phoenix colonies
Abstract
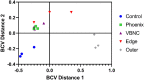
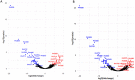
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a Gram-negative bacterium responsible for numerous human infections. Previously, novel antibiotic tolerant variants known as phoenix colonies as well as variants similar to viable but non-culturable (VBNC) colonies were identified in response to high concentrations of aminoglycosides. In this study, the mechanisms behind phoenix colony and VBNC-like colony emergence were further explored using both whole genome sequencing and RNA sequencing. Phoenix colonies were found to have a single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) in the PA4673 gene, which is predicted to encode a GTP-binding protein. No SNPs were identified within VBNC-like colonies compared to the founder population. RNA sequencing did not detect change in expression of PA4673 but revealed multiple differentially expressed genes that may play a role in phoenix colony emergence. One of these differentially expressed genes, PA3626, encodes for a tRNA pseudouridine synthase which when knocked out led to a complete lack of phoenix colonies. Although not immediately clear whether the identified genes in this study may have interactions which have not yet been recognized, they may contribute to the understanding of how phoenix colonies are able to emerge and survive in the presence of antibiotic exposure.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Novel Aminoglycoside-Tolerant Phoenix Colony Variants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2020 Aug 20;64(9):e00623-20. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00623-20. Print 2020 Aug 20. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2020. PMID: 32540981 Free PMC article.
-
Gene expression profiles of Vibrio parahaemolyticus in viable but non-culturable state.FEMS Microbiol Ecol. 2015 May;91(5):fiv035. doi: 10.1093/femsec/fiv035. Epub 2015 Apr 2. FEMS Microbiol Ecol. 2015. PMID: 25873464
-
Transcriptome analysis and prediction of the metabolic state of stress-induced viable but non-culturable Bacillus subtilis cells.Sci Rep. 2022 Oct 26;12(1):18015. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-21102-w. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36289289 Free PMC article.
-
[Viable non-culturable bacteria].Bacteriol Virusol Parazitol Epidemiol. 2010 Jan-Mar;55(1):11-8. Bacteriol Virusol Parazitol Epidemiol. 2010. PMID: 21038700 Review. Romanian.
-
Relationship between the Viable but Nonculturable State and Antibiotic Persister Cells.J Bacteriol. 2018 Sep 24;200(20):e00249-18. doi: 10.1128/JB.00249-18. Print 2018 Oct 15. J Bacteriol. 2018. PMID: 30082460 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Use of Dissolvable Synthetic Calcium Impregnated with Antibiotic in Osteoarticular Infection in Patients with Diabetes.Life (Basel). 2024 Oct 20;14(10):1335. doi: 10.3390/life14101335. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39459635 Free PMC article.
-
Inducible Mega-Mediated Macrolide Resistance Confers Heteroresistance in Streptococcus pneumoniae.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2023 Mar 16;67(3):e0131922. doi: 10.1128/aac.01319-22. Epub 2023 Feb 27. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2023. PMID: 36847556 Free PMC article.
-
Killing of a Multispecies Biofilm Using Gram-Negative and Gram-Positive Targeted Antibiotic Released from High Purity Calcium Sulfate Beads.Microorganisms. 2023 Sep 12;11(9):2296. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11092296. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 37764142 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lewis K. Multidrug tolerance of biofilms and persister cells. Curr. Top Microbiol. Immunol. 2008;322:107–131. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

