Delta variant (B.1.617.2) of SARS-CoV-2: current understanding of infection, transmission, immune escape, and mutational landscape
- PMID: 35962276
- PMCID: PMC9374302
- DOI: 10.1007/s12223-022-01001-3
Delta variant (B.1.617.2) of SARS-CoV-2: current understanding of infection, transmission, immune escape, and mutational landscape
Abstract
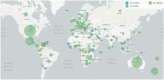
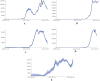
The Delta variant is one of the alarming variants of the SARS-CoV-2 virus that have been immensely detrimental and a significant cause of the prolonged pandemic (B.1.617.2). During the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic from December 2020 to October 2021, the Delta variant showed global dominance, and afterwards, the Omicron variant showed global dominance. Delta shows high infectivity rate which accounted for nearly 70% of the cases after December 2020. This review discusses the additional attributes that make the Delta variant so infectious and transmissible. The study also focuses on the significant mutations, namely the L452R and T478K present on the receptor-binding domain of spike (S)-glycoprotein, which confers specific alterations to the Delta variant. Considerably, we have also highlighted other notable factors such as the immune escape, infectivity and re-infectivity, vaccine escape, Ro number, S-glycoprotein stability, cleavage pattern, and its binding affinity with the host cell receptor protein. We have also emphasized clinical manifestations, symptomatology, morbidity, and mortality for the Delta variant compared with other significant SARS-CoV-2 variants. This review will help the researchers to get an elucidative view of the Delta variant to adopt some practical strategies to minimize the escalating spread of the SARS-CoV-2 Delta variant.
Keywords: Delta variant; Distribution; Immune escape; Infectivity; SARS-CoV-2.
© 2022. Institute of Microbiology, Academy of Sciences of the Czech Republic, v.v.i.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


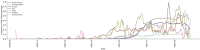

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

