Loneliness and academic performance mediates the relationship between fear of missing out and smartphone addiction among Iranian university students
- PMID: 35962328
- PMCID: PMC9372955
- DOI: 10.1186/s12888-022-04186-6
Loneliness and academic performance mediates the relationship between fear of missing out and smartphone addiction among Iranian university students
Abstract
Background: Fear of missing out (FoMO) can increase loneliness and smartphone addiction and decrease academic performance in university students. Most studies investigated the relationship between FoMO and smartphone addiction in developed countries, and no studies were found to examine this association in Iran. The mediating role of loneliness and academic performance in the relationship between FoMO and smartphone addiction is unclear. This study investigated the relationship between FoMO and smartphone addiction and the mediating role of loneliness and academic performance in this relationship in Iranian university students.
Methods: In this cross-sectional study, 447 students from Urmia University of Medical Sciences were investigated. Data were collected using demographic questionnaires, Przybylski's FoMO scale, Pham and Taylor's academic performance questionnaire, Russell's loneliness scale, and Kwon's smartphone addiction scale. Data were analyzed using SPSS ver. 23 and SmartPLS ver. 2.
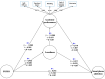
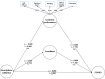
Results: FoMO had a positive and direct association with smartphone addiction (β = 0.315, t-value = 5.152, p < 0.01). FoMO also had a positive and direct association with students' loneliness (β = 0.432, t-value = 9.059, p < 0.01) and a negative and direct association with students' academic performance (β = -0.2602, t-value = 4.201, p < 0.01). FoMO indirectly associated with smartphone addiction through students' loneliness (β = 0.311, t-value = 5.075, p < 0.01), but academic performance was not mediator of smartphone addiction (β = 0.110, t-value = 1.807, p > 0.05). FoMO also indirectly correlated with academic performance through students' loneliness (β =-0.368, t-value = 6.377, p < 0.01).
Conclusions: FoMO can be positively associated with students' smartphone addiction, and loneliness is an important mediator of this association. Since smartphone addiction could harm students' academic performance, thus, healthcare administrators should reduce students' loneliness and improve their academic performance by adopting practical strategies to help students to manage their time and control their smartphone use. Holding self-management skills classes, keeping students on schedule, turning off smartphone notifications, encouraging students to engage in sports, and participating in group and family activities will help manage FoMO and loneliness.
Keywords: Academic performance; FoMO; Loneliness; Messaging applications; Smartphone addiction; Social network; Students.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Busch PA, McCarthy S. Antecedents and consequences of problematic smartphone use: A systematic literature review of an emerging research area. Comput Hum Behav. 2021;114:106414. doi: 10.1016/j.chb.2020.106414. - DOI
-
- Elhai JD, Yang H, Levine JC: Applying fairness in labeling various types of internet use disorders.•: Commentary on How to overcome taxonomical problems in the study of internet use disorders and what to do with “smartphone addiction”? Journal of Behavioral Addictions 2021, 9(4):924–927. 10.1556/2006.2020.00071 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mahapatra S. Smartphone addiction and associated consequences: Role of loneliness and self-regulation. Behaviour & Information Technology. 2019;38(8):833–844. doi: 10.1080/0144929X.2018.1560499. - DOI
-
- Sunday OJ, Adesope OO, Maarhuis PL. The effects of smartphone addiction on learning: A meta-analysis. Computers in Human Behavior Reports. 2021;4:100114. doi: 10.1016/j.chbr.2021.100114. - DOI
-
- Bhore NP. The Offshoots of Technology. International Journal of Psychiatric Nursing. 2017;3(1):142–145. doi: 10.5958/2395-180X.2017.00008.1. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources