The optimal screw-hole positions of the eccentric revision cup based on a morphological study
- PMID: 35962392
- PMCID: PMC9373531
- DOI: 10.1186/s13018-022-03260-9
The optimal screw-hole positions of the eccentric revision cup based on a morphological study
Abstract
Background: Bridging bone defects in revision total hip arthroplasty is a challenge to orthopedic surgeons. The eccentric revision cup is a progression of jumbo cup. Our aim is to confirm the optimal screw-hole positions of the eccentric revision cup by morphological measurements of three-dimensional pelvic reconstruction.
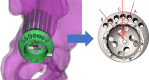
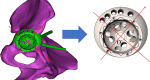
Methods: Eighty CT images were converted to virtual three-dimensional bones. After simulating the surgery procedure, all available screw holes were inserted with the screws in virtual. By measuring the length of the screw in the pelvic bone, we determined the rich bone stock area. Then the screw holes were designed according to the characteristics of bone stock distribution. The peripheral screw-hole cluster and inner screw-hole cluster were studied respectively.
Results: For peripheral screw-hole cluster, five screw holes were evenly distributed between point A and point B in the thicker rim. For inner screw-hole cluster, screw hole 1 and screw hole 2 are the recommended inner screw holes.
Conclusion: The eccentric revision cup has inherited the strengths of jumbo cup besides several unique advantages, including using the peripheral screws enhancing primary stability; decreasing the shift of hip rotation center and restoring biomechanical function; reducing the risk of dislocation because of the smaller head-cup differences; increasing the contact area between the outer cup and the host bone while maintaining a normal inclination of the inner cup. In this study, we confirmed the optimal screw-hole positions of the eccentric revision cup by surgical simulation and morphological measurement. However, biomechanical tests are still being further explored.
Keywords: Bone defect; Eccentric revision cup; Revision; Screw; Total hip arthroplasty.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- Brooks PJ. The jumbo cup: the 95% solution. Orthopedics. 2008;31(9):913. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

