Psychometric properties of Persian version of depression literacy (D-Lit) questionnaire among general population
- PMID: 35962416
- PMCID: PMC9372931
- DOI: 10.1186/s13033-022-00550-x
Psychometric properties of Persian version of depression literacy (D-Lit) questionnaire among general population
Abstract
Background: The prevalence of depression in society is increasing and there is a need for a suitable tool to assess the health literacy of people in this field. This study was conducted to evaluate the psychometric of the Iranian version of the depression literacy (D-Lit) questionnaire.
Methods: This cross-sectional study was conducted on 845 participants with a proportional stratified sampling method. First, the translation and cultural adaptation of questionnaire was performed. Then, the validity of D-Lit was assessed by face validity, content validity, exploratory factor analysis (EFA), and confirmatory factor analysis (CFA). The reliability of D-Lit was assessed by the Cronbach's alpha coefficient and McDonald omega coefficient.
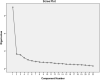
Results: Based on the results of EFA, 5 factors emerged with eigenvalues of greater than 1, which accounted for 56.30% of the variance. Based on the results of CFA, one question was deleted and the results of goodness fit indexes confirmed the model. Cronbach's alpha coefficient and McDonald omega coefficient for D-Lit questionnaire were 0.890 and 0.891, respectively. Finally, D-Lit questionnaire with 21 questions and 5 subscales of Knowledge of the psychological symptoms (5 items), Knowledge about the effectiveness of available treatment methods (4 items), Knowledge about cognitive-behavioral symptoms (6 items), Knowledge about taking medications and their side effects (4 items), and Knowledge of the severity of the disease (2 items) were confirmed.
Conclusion: The results of this psychometric evaluation confirmed the Persian version of D-Lit questionnaire with 21 questions and 5 subscales is an appropriate tool for measuring people's literacy about depression.
Keywords: Depression literacy (D-Lit); Mental Health; Mental health literacy; Reliability; Validity.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization . Depression and other common mental disorders: global health estimates. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2017.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

