Nanosecond electric pulses are equally effective in electrochemotherapy with cisplatin as microsecond pulses
- PMID: 35962956
- PMCID: PMC9400447
- DOI: 10.2478/raon-2022-0028
Nanosecond electric pulses are equally effective in electrochemotherapy with cisplatin as microsecond pulses
Abstract
Background: Nanosecond electric pulses showed promising results in electrochemotherapy, but the underlying mechanisms of action are still unexplored. The aim of this work was to correlate cellular cisplatin amount with cell survival of cells electroporated with nanosecond or standardly used 8 × 100 μs pulses and to investigate the effects of electric pulses on cisplatin structure.
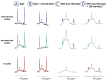
Materials and methods: Chinese hamster ovary CHO and mouse melanoma B16F1 cells were exposed to 1 × 200 ns pulse at 12.6 kV/cm or 25 × 400 ns pulses at 3.9 kV/cm, 10 Hz repetition rate or 8 × 100 μs pulses at 1.1 (CHO) or 0.9 (B16F1) kV/cm, 1 Hz repetition rate at three cisplatin concentrations. Cell survival was determined by the clonogenic assay, cellular platinum was measured by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Effects on the structure of cisplatin were investigated by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy and high-resolution mass spectrometry.
Results: Nanosecond pulses equivalent to 8 × 100 μs pulses were established in vitro based on membrane permeabilization and cell survival. Equivalent nanosecond pulses were equally efficient in decreasing the cell survival and accumulating cisplatin intracellularly as 8 × 100 μs pulses after electrochemotherapy. The number of intracellular cisplatin molecules strongly correlates with cell survival for B16F1 cells, but less for CHO cells, implying the possible involvement of other mechanisms in electrochemotherapy. The high-voltage electric pulses did not alter the structure of cisplatin.
Conclusions: Equivalent nanosecond pulses are equally effective in electrochemotherapy as standardly used 8 × 100 μs pulses.
Keywords: cisplatin; electrochemotherapy; electroporation; nanosecond pulses.
© 2022 Angelika Vizintin, Stefan Markovic, Janez Scancar, Jerneja Kladnik, Iztok Turel, Damijan Miklavcic, published by Sciendo.
Figures




References
-
- Campana LG, Miklavčič D, Bertino G, Marconato R, Valpione S, Imarisio I. Electrochemotherapy of superficial tumors – Current status: basic principles, operating procedures, shared indications, and emerging applications. Semin Oncol. 2019;46:173–91. doi: 10.1053/j.seminoncol.2019.04.002. M, et al. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

