The efficiency of health resource allocation and its influencing factors: evidence from the super efficiency slack based model-Tobit model
- PMID: 35963775
- PMCID: PMC10153566
- DOI: 10.1093/inthealth/ihac054
The efficiency of health resource allocation and its influencing factors: evidence from the super efficiency slack based model-Tobit model
Abstract
Background: This study aims to analyze the health resource allocation efficiency in Sichuan Province from 2010 to 2018 and provide other countries with China's experience.
Methods: We used the super efficiency slack based model (SBM) model and Malmquist index to analyze the super efficiency and inter-period efficiency of health resource allocation in 19 cities in Sichuan Province from 2010 to 2018 and propose the input-output optimization scheme of health resource allocation in 2018. Finally, the Tobit model was used to estimate the influencing factors of health resource allocation efficiency.
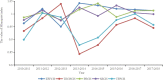
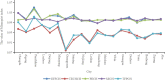
Results: The total allocation of health resources in Sichuan Province was increasing in addition to the total number of visits from 2010 to 2018. The super efficiency SBM results identified that the sample's average score was between 0.651 and 3.244, with an average of 1.041, of which 15 cities had not reached data envelopment analysis effectiveness. According to the Malmquist index, the average total factor productivity index of Sichuan Province was 0.930, which showed an imbalance in resource input, and its fluctuation was mainly related to the technological progress index and scale efficiency. The efficiency score was affected by the average annual income of residents, population density and education level.
Conclusions: The amount of health resource allocation in Sichuan Province had shown an overall upward trend since 2010. However, resource allocation efficiency was not high, and there were problems such as significant regional differences, insufficient technological innovation capabilities and unscientific allocation of resource scale. To optimize the resource allocation structure, we suggest that the relevant departments pay attention to the impact of natural disasters, the average annual income of residents, population density and education level on efficiency to allocate health resources scientifically.
Keywords: Malmquist index model; Tobit model; healthcare resource; productivity; super efficiency SBM model.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Investigating the efficiency of medical and health resources and its influencing factors in the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomerations: based on the undesirable super-efficiency SBM-Malmquist-Tobit model.Front Public Health. 2025 May 9;13:1527424. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1527424. eCollection 2025. Front Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40416655 Free PMC article.
-
Health expenditure efficiency in rural China using the super-SBM model and the Malmquist productivity index.Int J Equity Health. 2019 Jul 19;18(1):111. doi: 10.1186/s12939-019-1003-5. Int J Equity Health. 2019. PMID: 31324184 Free PMC article.
-
Efficiency analysis of primary health care resources: DEA and Tobit regression evidence from village clinics in Jiangsu Province.Front Public Health. 2025 Apr 23;13:1515532. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1515532. eCollection 2025. Front Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40337730 Free PMC article.
-
Study on the allocation efficiency of medical and health resources in Hainan Province: Based on the super-efficiency SBM-Malmquist model.PLoS One. 2024 Feb 29;19(2):e0294774. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0294774. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38421971 Free PMC article.
-
Spatio-temporal evolution and its policy influencing factors of agricultural land-use efficiency under carbon emission constraint in mainland China.Heliyon. 2024 Feb 9;10(4):e25816. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e25816. eCollection 2024 Feb 29. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38379967 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Can Comprehensive Medical Reform Improve the Efficiency of Medical Resource Allocation? Evidence From China.Int J Public Health. 2023 Dec 21;68:1606602. doi: 10.3389/ijph.2023.1606602. eCollection 2023. Int J Public Health. 2023. PMID: 38179320 Free PMC article.
-
Spatial distribution patterns of human resources allocation in maternal and child healthcare institutions in China from 2016 to 2021.BMC Health Serv Res. 2024 Jun 13;24(1):726. doi: 10.1186/s12913-024-11153-2. BMC Health Serv Res. 2024. PMID: 38872151 Free PMC article.
-
Coupling coordination relationship between health resource allocation and regional economic development: an empirical study based on five provinces in eastern China.Front Public Health. 2024 Dec 16;12:1513188. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1513188. eCollection 2024. Front Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39737454 Free PMC article.
-
How efficient are specialized public health services in China? A data envelopment analysis and geographically weighted regression approach.Front Public Health. 2025 Feb 12;13:1481402. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1481402. eCollection 2025. Front Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40013027 Free PMC article.
-
Estimating the Distribution and Convergence of County-level Healthcare Resources Allocative Efficiency in China Based on DEA and Spatial Panel Model.Inquiry. 2023 Jan-Dec;60:469580231178122. doi: 10.1177/00469580231178122. Inquiry. 2023. PMID: 37300427 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Liu GG, Vortherms SA, Hong X. China's Health Reform Update. Annu Rev Publ Health. 2017;38(1):431–48. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources