Gut microbes regulate the feeding center: a new discovery of Gut Brain Axis
- PMID: 35963865
- PMCID: PMC9376083
- DOI: 10.1038/s41392-022-01117-5
Gut microbes regulate the feeding center: a new discovery of Gut Brain Axis
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests
Figures
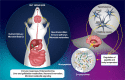
Comment on
-
Bacterial sensing via neuronal Nod2 regulates appetite and body temperature.Science. 2022 Apr 15;376(6590):eabj3986. doi: 10.1126/science.abj3986. Epub 2022 Apr 15. Science. 2022. PMID: 35420957
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

