A vegan diet improves insulin resistance in individuals with obesity: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 35964120
- PMCID: PMC9375406
- DOI: 10.1186/s13098-022-00879-w
A vegan diet improves insulin resistance in individuals with obesity: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: A vegan diet has benefits on weight reduction and on the parameters of glucose and lipid metabolism. This meta-analysis aimed to investigate the efficacy of plant-based diets on insulin resistance and blood lipids in patients with obesity.
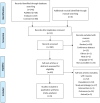
Methods: PubMed, Embase, and the Cochrane Library were searched for available papers published up to March 2021. The primary outcome was insulin resistance which was assessed by Homeostasis Model Assessment Insulin Resistance (HOMA-IR), other metabolic parameters measures including the pre/post-diet changes in triglycerides, HDL-cholesterol, total cholesterol, LDL-cholesterol. All analyses were performed using the random-effects model.
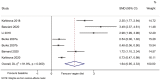
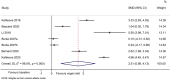
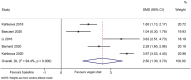
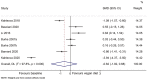
Results: Six studies (seven datasets) were included. Compared with baseline, the plant-based diet improved the HOMA-IR (SMD = 1.64, 95%CI 0.95, 2.33; I2 = 91.8%, Pheterogeneity < 0.001), total cholesterol (SMD = 2.51, 95% CI 0.88, 4.13; I2 = 98.0%, Pheterogeneity < 0.001), HDL-cholesterol (SMD = 1.55, 95% CI 0.66, 2.44; I2 = 92.0%, Pheterogeneity < 0.001), and LDL-cholesterol (SMD = 2.50, 95% CI 1.30, 3.70; I2 = 94.4%, Pheterogeneity < 0.001), but not the triglycerides (SMD = - 0.62, 95% CI - 1.92, 0.68; I2 = 97.8%, Pheterogeneity < 0.001). The sensitivity analyses showed that the results were robust.
Conclusions: In obese individuals with insulin resistance, a vegan diet improves insulin resistance and dyslipidemia, except for triglycerides.
Keywords: Insulin resistance; Meta-analysis; Obesity; Type 2 diabetes mellitus; Vegan diet.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The effects of ginger intake on weight loss and metabolic profiles among overweight and obese subjects: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2019;59(11):1753-1766. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2018.1427044. Epub 2018 Feb 2. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2019. PMID: 29393665
-
The Effects of Synbiotic Supplementation on Glucose Metabolism and Lipid Profiles in Patients with Diabetes: a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2018 Jun;10(2):329-342. doi: 10.1007/s12602-017-9299-1. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2018. PMID: 28677046
-
Effect of a Low-Fat Vegan Diet on Body Weight, Insulin Sensitivity, Postprandial Metabolism, and Intramyocellular and Hepatocellular Lipid Levels in Overweight Adults: A Randomized Clinical Trial.JAMA Netw Open. 2020 Nov 2;3(11):e2025454. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.25454. JAMA Netw Open. 2020. PMID: 33252690 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Apelin levels in pregnant women with and without gestational diabetes mellitus: a collaborative systematic review and meta-analysis.Gynecol Endocrinol. 2022 Oct;38(10):803-812. doi: 10.1080/09513590.2022.2114450. Epub 2022 Aug 24. Gynecol Endocrinol. 2022. PMID: 36002980
-
Hyperinsulinemia, insulin resistance and colorectal adenomas: A meta-analysis.Metabolism. 2015 Oct;64(10):1324-33. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2015.06.013. Epub 2015 Jun 20. Metabolism. 2015. PMID: 26169471
Cited by
-
Lifestyle Interventions for Treatment and Remission of Type 2 Diabetes and Prediabetes in Adults: A Clinical Practice Guideline From the American College of Lifestyle Medicine.Am J Lifestyle Med. 2025 Jun 10;19(2 Suppl):10S-131S. doi: 10.1177/15598276251325488. eCollection 2025 Jul. Am J Lifestyle Med. 2025. PMID: 40546761
-
Remission of Type 2 Diabetes After Treatment With a High-Fiber, Low-Fat, Plant-Predominant Diet Intervention: A Case Series.Am J Lifestyle Med. 2023 Jun 15;17(6):839-846. doi: 10.1177/15598276231181574. eCollection 2023 Nov-Dec. Am J Lifestyle Med. 2023. PMID: 38511112 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jensen MD, Ryan DH, Apovian CM, Ard JD, Comuzzie AG, Donato KA, et al. 2013 AHA/ACC/TOS guideline for the management of overweight and obesity in adults: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines and The Obesity Society. Circulation. 2014;129:S102–S138. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.0000437739.71477.ee. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Garvey WT, Mechanick JI, Brett EM, Garber AJ, Hurley DL, Jastreboff AM, et al. American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and American College of Endocrinology Comprehensive Clinical Practice Guidelines for Medical Care of Patients with Obesity. Endocr Pract. 2016;22(Suppl 3):1–203. doi: 10.4158/EP161365.GL. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

