Stability, survival, and patient satisfaction with CAD/CAM versus conventional multistranded fixed retainers in orthodontic patients: a 6-month follow-up of a two-centre randomized controlled clinical trial
- PMID: 35964235
- PMCID: PMC9912708
- DOI: 10.1093/ejo/cjac042
Stability, survival, and patient satisfaction with CAD/CAM versus conventional multistranded fixed retainers in orthodontic patients: a 6-month follow-up of a two-centre randomized controlled clinical trial
Abstract
Objectives: The primary aim of this two-arm parallel two-centre randomized controlled trial was to compare computer-aided design and computer-aided manufacturing (CAD/CAM) versus conventional multistranded fixed retainers (FRs) in terms of stability over 6 months. Secondary outcomes were failure rates and patient satisfaction.
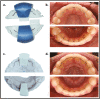
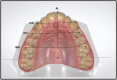
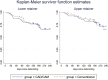
Methods: Patients were randomized to CAD/CAM or conventional FRs in both arches, in 1:1 ratio and blocks of four. Allocation concealment was secured by using sequentially numbered envelopes. Patients were blinded. Retainers were bonded at the end of orthodontic treatment (T0), and patients were recalled after 1 (T1), 3 (T3), and 6 (T6) months. First-time retainer failures were recorded and digital impressions were taken. Arch widths and lengths, as well as Little's Irregularity Index (LII), were measured. Additionally, patients answered satisfaction questionnaires. Linear mixed models were applied for measurements and patient satisfaction. Survival analyses were estimated with Kaplan-Meier curves, along with Cox-regression modelling.
Results: One hundred and eighty-one patients were randomized (98 in Centre 1, and 83 in Centre 2): Ninety in the CAD/CAM group and 91 in the conventional group. Three subjects dropped out at baseline, as they did not attend any of the follow-up appointments.168 patients attended the T6 visit. There were no significant differences in arch dimensions between T0 and T6, whilst the LII was different only in the CAD/CAM group (mean difference: 0.2 mm; 95% confidence interval: 0.1 to 0.4; P < 0.001). Within 6 months, 39 upper retainers (19 out of 88 CAD/CAM and 20 out of 90 conventional retainers) and 52 lower retainers failed (26 out of 88 CAD/CAM and 26 out of 90 conventional retainers), with no significant difference between the survival of both types of retainers (hazard ratios conventional to CAD/CAM: upper arch: 0.99 [P =0.99], lower arch: 0.93 [P = 0.80]). There were no significant changes in patient satisfaction between the groups. No harms were observed.
Conclusions: There were no clinically significant differences in LII, arch widths and lengths between CAD/CAM and conventional retainers after 6 months. There was no difference in failures and in patient satisfaction between both types of FRs.
Registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT04389879.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Orthodontic Society.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Stability, survival, patient satisfaction, and cost-minimization of CAD/CAM versus conventional multistranded fixed retainers in orthodontic patients: a 2-year follow-up of a two-centre randomized controlled trial.Eur J Orthod. 2024 Apr 1;46(2):cjae006. doi: 10.1093/ejo/cjae006. Eur J Orthod. 2024. PMID: 38394353 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Relapse and failure rates between CAD/CAM and conventional fixed retainers: a 2-year follow-up of a randomized controlled clinical trial.Eur J Orthod. 2024 Jan 1;46(1):cjad079. doi: 10.1093/ejo/cjad079. Eur J Orthod. 2024. PMID: 38168815 Clinical Trial.
-
Comparative assessment of relapse and failure between CAD/CAM stainless steel and standard stainless steel fixed retainers in orthodontic retention patients.Angle Orthod. 2022 Jan 1;92(1):87-94. doi: 10.2319/121720-1015.1. Angle Orthod. 2022. PMID: 34464438 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Can vacuum-formed retainers maintain arch dimensions and alignment compared to Hawley and fixed bonded retainers after treatment with fixed appliances? A systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur J Orthod. 2024 Oct 1;46(5):cjae040. doi: 10.1093/ejo/cjae040. Eur J Orthod. 2024. PMID: 39177154
-
Efficacy of CAD/CAM Technology in Interventions Implemented in Orthodontics: A Scoping Review of Clinical Trials.Biomed Res Int. 2022 Jun 2;2022:5310555. doi: 10.1155/2022/5310555. eCollection 2022. Biomed Res Int. 2022. PMID: 35692590 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Striving for Perfection: How Stable Is Orthodontic Treatment When Excellent Outcomes Are Achieved? A 9-Year Post-Treatment Retrospective Study.J Clin Med. 2023 Dec 14;12(24):7692. doi: 10.3390/jcm12247692. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 38137761 Free PMC article.
-
Debonding forces and failure modes of customized three-dimensional printed nano-ceramic hybrid resin fixed lingual retainers.J Orthod Sci. 2025 Mar 25;14:2. doi: 10.4103/jos.jos_75_24. eCollection 2025. J Orthod Sci. 2025. PMID: 40302879 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel 3-Dimensional Printed Nanoceramic Hybrid Resin Fixed Lingual Retainer: Characterization and Mechanical Tests.Int J Dent. 2024 Oct 15;2024:3540846. doi: 10.1155/2024/3540846. eCollection 2024. Int J Dent. 2024. PMID: 39445113 Free PMC article.
-
The prevalence of the failure of fixed orthodontic bonded retainers: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur J Orthod. 2023 Nov 30;45(6):645-661. doi: 10.1093/ejo/cjad047. Eur J Orthod. 2023. PMID: 37824794 Free PMC article.
-
Keeping the teeth in line: Exploring the necessity of bonded retainers in orthodontics: A narrative review.J Orthod Sci. 2024 May 8;13:20. doi: 10.4103/jos.jos_159_23. eCollection 2024. J Orthod Sci. 2024. PMID: 38784083 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Papagiannis, A., Koletsi, D., Halazonetis, D.J. and Sifakakis, I. (2021) Relapse 1 week after bracket removal: a 3D superimpositional analysis. European Journal of Orthodontics, 43, 128–135. - PubMed
-
- Littlewood, S.J., Millett, D.T., Doubleday, B., Bearn, D.R. and Worthington, H.V. (2016) Retention procedures for stabilising tooth position after treatment with orthodontic braces. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, 2016, CD002283. - PubMed
-
- Bearn, D.R. (1995) Bonded orthodontic retainers: a review. American Journal of Orthodontics and Dentofacial Orthopedics, 108, 207–213. - PubMed
-
- Renkema, A.M., Sips, E.T., Bronkhorst, E. and Kuijpers-Jagtman, A.M. (2009) A survey on orthodontic retention procedures in The Netherlands. European Journal of Orthodontics, 31, 432–437. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

