Questioning ZnO, Ag, and Ag/ZnO nanoparticles as antimicrobial agents for textiles: Do they guarantee total protection against bacteria and SARS-CoV-2?
- PMID: 35964336
- PMCID: PMC9349053
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2022.112538
Questioning ZnO, Ag, and Ag/ZnO nanoparticles as antimicrobial agents for textiles: Do they guarantee total protection against bacteria and SARS-CoV-2?
Abstract
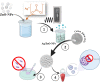
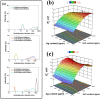
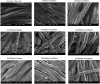
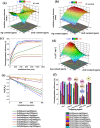
Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) occasioned global economic and health systems collapse. Also, it raised several concerns about using conventional cotton fabrics for manufacturing personal protective equipment without the antimicrobial capacity to inactivate viruses, such as Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and its variants. Therefore, developing antimicrobial cotton fibers is crucial to avoid new global pandemics or the transmission of dangerous pathogens that remain on surfaces for long periods, especially in hospitals and medical clinics. Herein, we developed antimicrobial cotton fabrics with Ag, ZnO, and Ag/ZnO nanoparticles and evaluated their bactericidal activity against Escherichia coli (E. coli) and Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus), photocatalytic activity, and antiviral activity against Delta SARS-CoV-2. Although the antimicrobial fabrics are effective against these bacteria, they only reduce part of the SARS-CoV-2 virions during the first 15 min of direct contact via damage only to biological structures on the viral surface particle while the viral RNA remains intact.
Keywords: Antimicrobial; Multifunctional textiles; SARS-CoV-2; Silver; ZnO.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
-
- Magurano F., Baggieri M., Marchi A., Rezza G., Nicoletti L., Eleonora B., Concetta F., Stefano F., Maedeh K., Paola B., Emilio D., Silvia G. SARS-CoV-2 infection: the environmental endurance of the virus can be influenced by the increase of temperature. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2021;27(289):e5–289.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2020.10.034. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

