Bulk phase biochemistry of PIF1 and RecQ4 family helicases
- PMID: 35965006
- PMCID: PMC9382717
- DOI: 10.1016/bs.mie.2022.03.031
Bulk phase biochemistry of PIF1 and RecQ4 family helicases
Abstract
DNA helicases are involved in nearly all facets of genome integrity, and in humans, mutations in helicase-encoding genes are often linked to diseases of genomic instability. Two highly studied and evolutionarily conserved helicase families are the PIF1 and RecQ helicases. Enzymes in these families have known roles in DNA replication, recombination, and repair, as well as telomere maintenance, DNA recombination, and transcription. Although genetics, structural biology, and a variety of other techniques have been used to study these helicases, ensemble analyses of their basic biochemical activities such as DNA binding, ATP hydrolysis, and DNA unwinding have made significant contributions to our understanding of their physiological roles. Here, we present general methods to generate recombinant proteins from both helicase families, as well as standard biochemical assays to investigate their activities on DNA.
Keywords: ATPase; DNA binding; Helicase; Hrq1; PIF1; RecQ.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
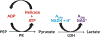
References
-
- Bachrati CZ, & Hickson ID (2008). RecQ helicases: Guardian angels of the DNA replication fork. Chromosoma, 117, 219–233. Retrieved from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=PubMed&dop.... - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

