D-dopachrome tautomerase drives astroglial inflammation via NF-κB signaling following spinal cord injury
- PMID: 35965310
- PMCID: PMC9375920
- DOI: 10.1186/s13578-022-00867-7
D-dopachrome tautomerase drives astroglial inflammation via NF-κB signaling following spinal cord injury
Abstract
Background: Reactive astrocytes are increasingly recognized as crucial regulators of innate immunity in degenerative or damaged central nervous system (CNS). Many proinflammatory mediators have been shown to drive inflammatory cascades of astrocytes through activation of NF-κB, thereby affecting the functional outcome of the insulted CNS. D-dopachrome tautomerase (D-DT), a newly described cytokine and a close homolog of proinflammatory macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF), has been revealed to share receptor and overlapping functional spectrum with MIF, but little is known about its roles in the neuropathological progression of the CNS and relevant regulatory mechanisms.
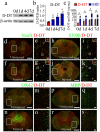
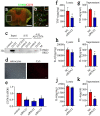
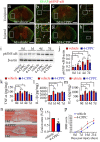
Results: D-DT protein levels were significantly elevated within neurons and astrocytes following SCI. Analysis of transcriptome profile revealed that D-DT was able to activate multiple signal pathways of astrocytes, which converged to NF-κB, a hub regulator governing proinflammatory response. Rat D-DT recombinant protein was efficient in inducing the production of inflammatory cytokines from astrocytes through interaction with CD74 receptor. Activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) and NF-κB was observed to be essential for the transduction of D-DT signaling. Administration of D-DT specific inhibitor at lesion sites of the cord resulted in significant attenuation of NF-κB activation and reduction of the inflammatory cytokines following SCI, and accordingly improved the recovery of locomotor functions.
Conclusion: Collectively, D-DT is a novel proinflammatory mediator of astrocytes following SCI. Insights of its cell-specific expression and relevant proinflammatory mechanisms will provide clues for the control of CNS inflammation.
Keywords: Astrocyte; Central nervous system; D-DT; Inflammation; MAPKs; NF-κB; Spinal cord injury.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures





References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

