SUPPRESSOR OF PHYTOCHROME B-4 #3 reduces the expression of PIF-activated genes and increases expression of growth repressors to regulate hypocotyl elongation in short days
- PMID: 35965321
- PMCID: PMC9377115
- DOI: 10.1186/s12870-022-03737-z
SUPPRESSOR OF PHYTOCHROME B-4 #3 reduces the expression of PIF-activated genes and increases expression of growth repressors to regulate hypocotyl elongation in short days
Abstract
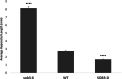
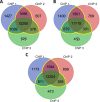
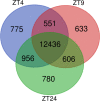
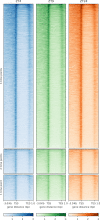
SUPPRESSOR OF PHYTOCHROME B-4 #3 (SOB3) is a member of the AT-HOOK MOTIF CONTAINING NUCLEAR LOCALIZED (AHL) family of transcription factors that are involved in light-mediated growth in Arabidopsis thaliana, affecting processes such as hypocotyl elongation. The majority of the research on the AHLs has been conducted in continuous light. However, there are unique molecular events that promote growth in short days (SD) compared to constant light conditions. Therefore, we investigated how AHLs affect hypocotyl elongation in SD. Firstly, we observed that AHLs inhibit hypocotyl growth in SD, similar to their effect in constant light. Next, we identified AHL-regulated genes in SD-grown seedlings by performing RNA-seq in two sob3 mutants at different time points. Our transcriptomic data indicate that PHYTOCHROME INTERACTING FACTORS (PIFs) 4, 5, 7, and 8 along with PIF-target genes are repressed by SOB3 and/or other AHLs. We also identified PIF target genes that are repressed and have not been previously described as AHL-regulated, including PRE1, PIL1, HFR1, CDF5, and XTR7. Interestingly, our RNA-seq data also suggest that AHLs activate the expression of growth repressors to control hypocotyl elongation, such as HY5 and IAA17. Notably, many growth-regulating and other genes identified from the RNA-seq experiment were differentially regulated between these two sob3 mutants at the time points tested. Surprisingly, our ChIP-seq data suggest that SOB3 mostly binds to similar genes throughout the day. Collectively, these data suggest that AHLs affect gene expression in a time point-specific manner irrespective of changes in binding to DNA throughout SD.
Keywords: AHL; Arabidopsis; Hypocotyl; PIF; SD; SOB3.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures





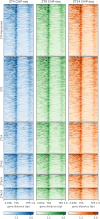
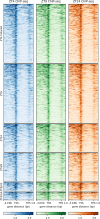
Similar articles
-
AT-Hook Transcription Factors Restrict Petiole Growth by Antagonizing PIFs.Curr Biol. 2020 Apr 20;30(8):1454-1466.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2020.02.017. Epub 2020 Mar 19. Curr Biol. 2020. PMID: 32197081
-
SUPPRESSOR OF PHYTOCHROME B4-#3 Represses Genes Associated with Auxin Signaling to Modulate Hypocotyl Growth.Plant Physiol. 2016 Aug;171(4):2701-16. doi: 10.1104/pp.16.00405. Epub 2016 Jun 24. Plant Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27342309 Free PMC article.
-
Arabidopsis thaliana AHL family modulates hypocotyl growth redundantly by interacting with each other via the PPC/DUF296 domain.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Nov 26;110(48):E4688-97. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1219277110. Epub 2013 Nov 11. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 24218605 Free PMC article.
-
Brassinosteroid signaling converges with SUPPRESSOR OF PHYTOCHROME B4-#3 to influence the expression of SMALL AUXIN UP RNA genes and hypocotyl growth.Plant J. 2017 Mar;89(6):1133-1145. doi: 10.1111/tpj.13451. Epub 2017 Feb 17. Plant J. 2017. PMID: 27984677 Free PMC article.
-
Circadian Waves of Transcriptional Repression Shape PIF-Regulated Photoperiod-Responsive Growth in Arabidopsis.Curr Biol. 2018 Jan 22;28(2):311-318.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2017.12.021. Epub 2018 Jan 11. Curr Biol. 2018. PMID: 29337078
Cited by
-
AHL26, an AT-hook gene, negatively regulates hypocotyl growth and flowering time in Arabidopsis thaliana.BMC Plant Biol. 2025 May 30;25(1):730. doi: 10.1186/s12870-025-06764-8. BMC Plant Biol. 2025. PMID: 40442601 Free PMC article.
-
The ability of Arabidopsis to recover from Basta and its application in isolating Cas9-free mutants.Front Plant Sci. 2024 Oct 16;15:1408230. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1408230. eCollection 2024. Front Plant Sci. 2024. PMID: 39479542 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Street IH, Shah PK, Smith AM, Avery N, Neff MM. The AT-hook-containing proteins SOB3/AHL29 and ESC/AHL27 are negative modulators of hypocotyl growth in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2008;54(1):1–14. 10.1111/j.1365-313x.2007.03393.x. - PubMed
-
- Xiao C, Chen F, Yu X, Lin C, Fu YF. Over-expression of an AT-hook gene, AHL22, delays flowering and inhibits the elongation of the hypocotyl in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Mol Biol. 2009;71:39–50. 10.1007/s11103-009-9507-9. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

