NLRP3 inflammasome up-regulates major histocompatibility complex class I expression and promotes inflammatory infiltration in polymyositis
- PMID: 35965334
- PMCID: PMC9375941
- DOI: 10.1186/s12865-022-00515-2
NLRP3 inflammasome up-regulates major histocompatibility complex class I expression and promotes inflammatory infiltration in polymyositis
Abstract
Objective: This study was designed to investigate the role of the nucleotide-binding-domain -and leucine-rich repeat -containing (NLR) family, pyrin-domain-containing 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome in the pathogenesis of polymyositis (PM).
Methods: Immunochemistry was performed to analyze the NLRP3, caspase-1 and interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β) expression in the muscle tissue of PM patients. Rat model of PM and C2C12 cell were used to investigate the potential role of NLRP3 inflammasome in PM.
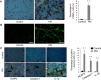
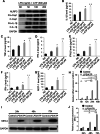
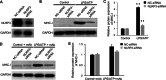
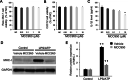
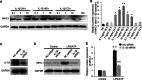
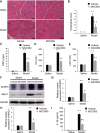
Results: The percentage of CD 68+ macrophages, and the expression levels of NLRP3, caspase-1 and IL-1β in the muscle tissue were elevated in 27 PM patients. LPS/ATP treatment resulted in activation of NLRP3 inflammasome and secretion of IL-1β as well as interferons (IFNs) and monocyte chemotactic protein-1 (MCP-1) in the Raw 264.7 macrophages. Meanwhile, LPS/ATP challenged activation of NLRP3 inflammasome induced overexpression of major histocompatibility complex class I (MHC-I), a key molecular of PM in the co-cultured C2C12 cells. The effect was decreased by treatment of NLRP3 inflammasome inhibitor MCC950 or siRNA of NLRP3 inflammasome. These findings suggested certain levels of IL-1β rather than IFNs up-regulated MHC-I expression in C2C12 cells. IL-1β blockade using neutralizing IL-1β monoclonal antibody or siRNA of IL-1β suppressed MHC-I overexpression. In vivo, NLRP3 inflammasome inhibition by MCC950 reduced the expression of NLRP3, IL-1β and MHC-I in the muscle tissue of PM modal rats. Also, it attenuated the intensity of muscle inflammation as well as the CRP, CK, and LDH levels in the serum.
Conclusion: NLRP3/caspase-1/IL-1β axis may play an important role in the development of PM. Inhibition of NLRP3 activation may hold promise in the treatment of PM.
Keywords: Autoimmune diseases; Inflammation; MCC950; Major histocompatibility complex class I; NLRP3 inflammasome; Polymyositis.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be constructed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Helmers SB, Bruton M, Loell I, Ulfgren AK, Gracie AJ, McInnes IB, et al. Expression of interleukin-18 in muscle tissue of patients with polymyositis or dermatomyositis and effects of conventional immunosuppressive treatment. Rheumatology. 2018;57:2149–2157. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/key222. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zhang SX, Wang J, Sun HH, Zhang JQ, Liu GY, Luo J, He P-F, Li X-F. Circulating regulatory T cells were absolutely decreased in dermatomyositis/polymyositis patients and restored by low-dose IL-2. Ann Rheum Dis. 2019;0:1–3. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

