Association of hyperuricemia with apolipoprotein AI and atherogenic index of plasma in healthy Chinese people: a cross-sectional study
- PMID: 35965341
- PMCID: PMC9377099
- DOI: 10.1186/s12872-022-02810-7
Association of hyperuricemia with apolipoprotein AI and atherogenic index of plasma in healthy Chinese people: a cross-sectional study
Abstract
Background: The atherogenic index of plasma (AIP) is a predictor for cardiovascular diseases (CVD), while hyperuricemia is an independent risk factor for a variety of CVD. Apolipoprotein AI has been found to be a protective factor for CVD. However, the role of APO AI in the association between plasma uric acid and AIP among healthy Chinese people needs to be further explored.
Aims: To evaluate the relationship between blood uric acid and AIP level in healthy Chinese people. To evaluate the relationship between blood uric acid and Apolipoprotein AI in healthy Chinese people.
Method: A total of 3501 normal and healthy subjects who had physical examinations were divided into the hyperuricemia (HUA) group and the normouricemia (NUA) group.
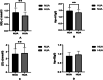
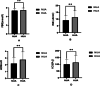
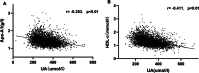
Result: The AIP of HUA group was significantly higher than that of NUA group [0.17±0.30 vs. -0.08±0.29]. Apo AI (1.33 ± 0.21 vs. 1.47 ± 0.26 g/l) and HDL-c (1.12 ± 0.27 vs. 1.36 ± 0.33 mmol/l) were significantly lower in the HUA group than in the NUA group. LDL-C (2.81 ± 0.77 vs. 2.69 ± 0.73 mmol/l), Apo B (0.96 ± 0.20 vs. 0.89 ± 0.20 g/l), FBG (5.48 ± 0.48 vs. 5.36 ± 0.48 mmol/l) and HOMA-IR [2.75 (1.92-3.91) vs. 2.18 (1.50-3.12)] was significantly higher in HAU group than the NUA group. Increases in plasma UA were associated with increases in AIP (β = 0.307, p < 0.01) and decreases in Apo AI (β = - 0.236, p < 0.01).
Conclusion: Hyperuricemia is an independent risk factor for high AIP level. Inhibition of Apolipoprotein AI may be one of the mechanisms of UA which is involved in the progression of cardiovascular disease.
Keywords: AIP; Apo AI; Hyperuricemia.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Anesthesiology NJSO. Serum uric acid and cardiovascular mortality: the NHANES I epidemiologic follow-up study, 1971–1992. Surv Anesthesiol. 2001;45(2):121–122. doi: 10.1097/00132586-200104000-00057. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

