Resident Immune Cells of the Liver in the Tumor Microenvironment
- PMID: 35965506
- PMCID: PMC9365660
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.931995
Resident Immune Cells of the Liver in the Tumor Microenvironment
Abstract
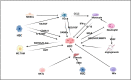
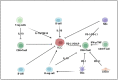
The liver is a central immunomodulator that ensures a homeostatic balance between protection and immunotolerance. A hallmark of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the deregulation of this tightly controlled immunological network. Immune response in the liver involves a complex interplay between resident innate, innate, and adaptive immune cells. The immune response in the liver is modulated by its continuous exposure to toxic molecules and microorganisms that requires a degree of immune tolerance to protect normal tissue from damage. In HCC pathogenesis, immune cells must balance a dual role that includes the elimination of malignant cells, as well as the repair of damaged liver tissue to maintain homeostasis. Immune response in the innate and adaptive immune systems extends to the cross-talk and interaction involving immune-regulating non-hematopoietic cells, myeloid immune cells, and lymphoid immune cells. In this review, we discuss the different immune responses of resident immune cells in the tumor microenvironment. Current FDA-approved targeted therapies, including immunotherapy options, have produced modest results to date for the treatment of advanced HCC. Although immunotherapy therapy to date has demonstrated its potential efficacy, immune cell pathways need to be better understood. In this review article, we summarize the roles of specific resident immune cell subsets and their cross-talk subversion in HCC pathogenesis, with a view to identifying potential new biomarkers and therapy options.
Keywords: adaptive; cells; immunology; innate; liver; tumorigenesis.
Copyright © 2022 Lu, Ma, Ding, Sun, Zhou, Duan and Sartorius.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The immunology of hepatocellular carcinoma.Nat Immunol. 2018 Mar;19(3):222-232. doi: 10.1038/s41590-018-0044-z. Epub 2018 Jan 29. Nat Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29379119 Review.
-
Revamping the innate or innate-like immune cell-based therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: new mechanistic insights and advanced opportunities.Med Oncol. 2023 Jan 21;40(2):84. doi: 10.1007/s12032-023-01948-4. Med Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36680649 Review.
-
Innate immune cells and their interaction with T cells in hepatocellular carcinoma.Oncol Lett. 2021 Jan;21(1):57. doi: 10.3892/ol.2020.12319. Epub 2020 Nov 19. Oncol Lett. 2021. PMID: 33281968 Free PMC article. Review.
-
From bench to bed: the tumor immune microenvironment and current immunotherapeutic strategies for hepatocellular carcinoma.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019 Sep 9;38(1):396. doi: 10.1186/s13046-019-1396-4. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31500650 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Liver immunotolerance and hepatocellular carcinoma: Patho-physiological mechanisms and therapeutic perspectives.Eur J Cancer. 2017 Dec;87:101-112. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2017.10.010. Epub 2017 Nov 13. Eur J Cancer. 2017. PMID: 29145036 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of dexmedetomidine on oxidative stress, programmed cell death, liver function, and expression of peripheral immune cells in patients with primary liver cancer undergoing hepatectomy.Front Physiol. 2023 Apr 11;14:1159746. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1159746. eCollection 2023. Front Physiol. 2023. PMID: 37113696 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of microRNAs in Hepatocellular Cancer: A Narrative Review Focused on Tumor Microenvironment and Drug Resistance.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2024 Jan-Dec;23:15330338241239188. doi: 10.1177/15330338241239188. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2024. PMID: 38634139 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NK cell marker gene-based model shows good predictive ability in prognosis and response to immunotherapies in hepatocellular carcinoma.Sci Rep. 2023 May 5;13(1):7294. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-34602-0. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37147523 Free PMC article.
-
Key oncogenic signaling pathways affecting tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes infiltration in hepatocellular carcinoma: basic principles and recent advances.Front Immunol. 2024 Feb 15;15:1354313. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1354313. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38426090 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immune Checkpoint Blockade: A Strategy to Unleash the Potential of Natural Killer Cells in the Anti-Cancer Therapy.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Oct 14;14(20):5046. doi: 10.3390/cancers14205046. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36291830 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

