Differential responses to 223Ra and Alpha-particles exposure in prostate cancer driven by mitotic catastrophe
- PMID: 35965568
- PMCID: PMC9367686
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.877302
Differential responses to 223Ra and Alpha-particles exposure in prostate cancer driven by mitotic catastrophe
Abstract
Introduction: Radium-223 (223Ra) has been shown to have an overall survival benefit in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC) involving bone. Despite its increased clinical usage, relatively little is known regarding the mechanism of action of 223Ra at the cellular level.
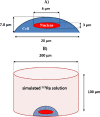
Methods: We evaluated the effects of 223Ra irradiation in a panel of cell lines and then compared them with standard X-ray and external alpha-particle irradiation, with a particular focus on cell survival and DNA damage repair kinetics.
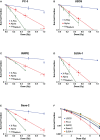
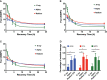
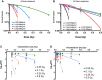
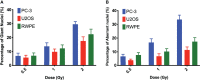
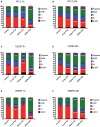
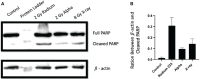
Results: 223Ra exposures had very high, cell-type-dependent RBE50% ranging from 7 to 15. This was significantly greater than external alpha irradiations (RBE50% from 1.4 to 2.1). These differences were shown to be partially related to the volume of 223Ra solution added, independent of the alpha-particle dose rate, suggesting a radiation-independent mechanism of effect. Both external alpha particles and 223Ra exposure were associated with delayed DNA repair, with similar kinetics. Additionally, the greater treatment efficacy of 223Ra was associated with increased levels of residual DNA damage and cell death by mitotic catastrophe.
Conclusions: These results suggest that 223Ra exposure may be associated with greater biological effects than would be expected by direct comparison with a similar dose of external alpha particles, highlighting important challenges for future therapeutic optimization.
Keywords: alpha particles; bone metastases; mitotic catastrophe; radiation effects; radium-223.
Copyright © 2022 Guerra Liberal, Moreira, Redmond, O’Sullivan, Alshehri, Wright, Dunne, Campfield, Biggart, McMahon and Prise.
Conflict of interest statement
JO’S has received honoraria as part of the speakers’ bureau and the advisory board of Bayer and has received institutional research funding from Bayer. KP has received speaker honoraria from Bayer. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

