A real-world study of anlotinib as third-line or above therapy in patients with her-2 negative metastatic breast cancer
- PMID: 35965587
- PMCID: PMC9366600
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.939343
A real-world study of anlotinib as third-line or above therapy in patients with her-2 negative metastatic breast cancer
Abstract
Background: Antiangiogenic agents provides an optional treatment strategy for patients with metastatic breast cancer. The present study was conducted to evaluate the efficacy and safety of anlotinib as third-line or above therapy for patients with HER-2 negative metastatic breast cancer.
Methods: Patients with HER-2 negative metastatic breast cancer who have failed from prior therapy and treated with anlotinib monotherapy or combined with chemotherapy or immunotherapy from June 2018 to December 2020 were retrospectively analyzed based on real-world clinical practice. The primary end point was progression free survival (PFS). Secondary end points included objective response rate (ORR), disease control rate (DCR), overall survival (OS) and safety.
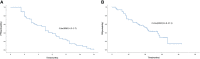
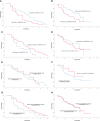
Results: 47 patients with HER-2 negative metastatic breast cancer received anlotinib monotherapy or combination therapy as third-line or above therapy. In the general population, 10 patients achieved PR, 25 patients had SD and 12 patients had PD. The overall ORR and DCR were 21.3% and 74.5%, respectively. Subgroup analysis suggested that there were no statistically significant differences in ORR and DCR with respect to HR status (positive vs. negative), treatment programs (monotherapy vs. combination) and treatment type in combination group (chemotherapy vs. immunotherapy). The patients who did not received previously anti-angiogenesis therapy had superior DCR (84.8% vs. 50.0%, P=0.012). Median PFS and OS were 5.0 months (95% CI=4.3-5.7) and 21.0 (95% CI=14.9-27.1) months, respectively. The PFS (6.5m vs. 3.5m, P=0.042)and OS (28.2m vs. 12.6m, P=0.040) were better in HR positive patients than HR negative patients. And simultaneously, patients who received anlotinib combination therapy obtained better PFS (5.5m vs. 3.0m, P=0.045). The incidence of Grade 3-4 adverse events(AEs) was 31.9%.
Conclusions: Anlotinib monotherapy or combination therapy provide a viable third-line or above therapeutic strategy in patients with HER-2 negative metastatic breast cancer, a median PFS of 5.0 months was obtained with well tolerated toxicity.
Keywords: anlotinib; anti-angiogenesis; breast cancer; immunotherapy; safety.
Copyright © 2022 Shao, Luo, Yu, He, Liu, Chen, Zhu, Nie and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Anlotinib in combination with metronomic chemotherapy in HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer: an observational and retrospective study.BMC Cancer. 2025 Jan 3;25(1):9. doi: 10.1186/s12885-024-13403-2. BMC Cancer. 2025. PMID: 39754078 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Study of Anlotinib as Third-Line or Above Therapy in Patients With Advanced or Metastatic Gastric Cancer: A Multicenter Retrospective Study.Front Oncol. 2022 Jul 4;12:885350. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.885350. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35860585 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of anlotinib in Chinese patients with metastatic breast cancer: A retrospective observational study.J Cell Mol Med. 2024 Mar;28(5):e18008. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.18008. Epub 2023 Oct 27. J Cell Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 37891706 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety evaluations of anlotinib in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer treated with bevacizumab.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Sep 27;13:973448. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.973448. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36238567 Free PMC article.
-
Anlotinib for refractory advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2020 Nov 30;15(11):e0242982. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0242982. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 33253313 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Anlotinib in combination with metronomic chemotherapy in HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer: an observational and retrospective study.BMC Cancer. 2025 Jan 3;25(1):9. doi: 10.1186/s12885-024-13403-2. BMC Cancer. 2025. PMID: 39754078 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of Anlotinib based neoadjuvant chemotherapy for locally advanced triple negative breast cancer (TNBC).BMC Cancer. 2024 Oct 7;24(1):1237. doi: 10.1186/s12885-024-12852-z. BMC Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39375657 Free PMC article.
-
Role of anlotinib plus albumin paclitaxel regimen in stage IV non-small cell lung cancer and mental state.World J Psychiatry. 2025 Aug 19;15(8):103735. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v15.i8.103735. eCollection 2025 Aug 19. World J Psychiatry. 2025. PMID: 40837809 Free PMC article.
-
A single-arm phase II clinical trial of anlotinib combined with chemotherapy for the treatment of metastatic triple-negative breast cancer.Front Oncol. 2023 Apr 12;13:1122294. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1122294. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37124484 Free PMC article.
-
Continuous Anlotinib Combined with Oral Vinorelbine has Shown Anti-Tumor Efficiency in Refractory HER2 Negative Advanced Breast Cancer.Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press). 2025 Jun 28;17:545-555. doi: 10.2147/BCTT.S534082. eCollection 2025. Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press). 2025. PMID: 40606069 Free PMC article.
References
-
- von Minckwitz G, Schneeweiss A, Loibl S, Salat C, Denkert C, Rezai M, et al. . Neoadjuvant carboplatin in patients with triple-negative and HER2-positive early breast cancer (GeparSixto; GBG 66): a randomised phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol (2014) 15(7):747–56. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(14)70160-3 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cortes J, Cescon DW, Rugo HS, Nowecki Z, Im SA, Yusof MM, et al. . Pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy versus placebo plus chemotherapy for previously untreated locally recurrent inoperable or metastatic triple-negative breast cancer (KEYNOTE-355): a randomised, placebo-controlled, double-blind, phase 3 clinical trial. Lancet. (2020) 396(10265):1817–28. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32531-9 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

