In silico Prediction of Deleterious Single Nucleotide Polymorphism in S100A4 Metastatic Gene: Potential Early Diagnostic Marker
- PMID: 35965620
- PMCID: PMC9357733
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/4202623
In silico Prediction of Deleterious Single Nucleotide Polymorphism in S100A4 Metastatic Gene: Potential Early Diagnostic Marker
Abstract
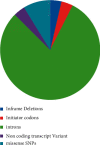
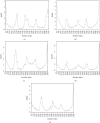
S100A4 protein overexpression has been reported in different types of cancer and plays a key role by interacting with the tumor suppressor protein Tp53. Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP) in S100A4 could directly influence the biomolecular interaction with the tumor suppressor protein Tp53 due to their aberrant conformations. Hence, the study was designed to predict the deleterious SNP and its effect on the S100A4 protein structure and function. Twenty-one SNP data sets were screened for nonsynonymous mutations and subsequently subjected to deleterious mutation prediction using different computational tools. The screened deleterious mutations were analyzed for their changes in functionality and their interaction with the tumor suppressor protein Tp53 by protein-protein docking analysis. The structural effects were studied using the 3DMissense mutation tool to estimate the solvation energy and torsion angle of the screened mutations on the predicted structures. In our study, 21 deleterious nonsynonymous mutations were screened, including F72V, E74G, L5P, D25E, N65S, A28V, A8D, S20L, L58P, and K26N were found to be remarkably conserved by exhibiting the interaction either with the EF-hand 1 or EF-hand 2 domain. The solvation and torsion values significantly deviated for the mutant-type structures with S20L, N65S, and F72L mutations and showed a marked reduction in their binding affinity with the Tp53 protein. Hence, these deleterious mutations might serve as prospective targets for diagnosing and developing personalized treatments for cancer and other related diseases.
Copyright © 2022 Aisha Farhana et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

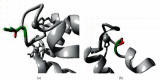

Similar articles
-
S100a4 upregulation in Pik3caH1047R;Trp53R270H;MMTV-Cre-driven mammary tumors promotes metastasis.Breast Cancer Res. 2019 Dec 27;21(1):152. doi: 10.1186/s13058-019-1238-5. Breast Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31881983 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of the TP53 Deleterious Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms Impact on Estrogen Receptor Alpha-p53 Interaction: A Machine Learning Approach.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jun 18;20(12):2962. doi: 10.3390/ijms20122962. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31216622 Free PMC article.
-
The C-terminal region of S100A4 is important for its metastasis-inducing properties.Oncogene. 2005 Jun 23;24(27):4401-11. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1208663. Oncogene. 2005. PMID: 15856021
-
Metastasis-associated protein S100A4: spotlight on its role in cell migration.Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2007 May;7(3):217-28. doi: 10.2174/156800907780618329. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2007. PMID: 17504119 Review.
-
The Multifaceted S100A4 Protein in Cancer and Inflammation.Methods Mol Biol. 2019;1929:339-365. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-9030-6_22. Methods Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 30710284 Review.
References
-
- Rudland P. S., Platt-Higgins A., Renshaw C., et al. Prognostic significance of the metastasis-inducing protein S100A4 (p9Ka) in human breast cancer. Cancer Research . 2000;60(6):1595–1603. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
