Investigation of proteins' interaction network and the expression pattern of genes involved in the ABA biogenesis and antioxidant system under methanol spray in drought-stressed rapeseed
- PMID: 35965657
- PMCID: PMC9365922
- DOI: 10.1007/s13205-022-03290-4
Investigation of proteins' interaction network and the expression pattern of genes involved in the ABA biogenesis and antioxidant system under methanol spray in drought-stressed rapeseed
Abstract
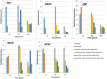
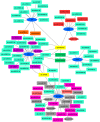
Drought is one of the most critical abiotic stresses, which significantly impair rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) productivity. Several factors can regulate the stress response, including changes in gene expression in biological pathways, extensive protein interaction networks, and post-translational regulatory factors like microRNAs. External factors can also affect the intensity of the stress response. Therefore, this study investigated protein-protein interactions of some essential genes involved in abscisic acid (ABA) production, antioxidant system, and Krebs cycle. The expression of phyton synthase (PSY), 9-cis-epoxycarotenoid dioxygenase (NCED3), aldehyde oxidase (AAO3), thioredoxin reductase (NTRC), and glutathione reductase (GR) genes in two rapeseed genotypes, i.e., Hyola308 (drought-sensitive) and SLM046 (drought-tolerant) were evaluated using qRT-PCR technique under 72 h of drought stress and methanol foliar application. In the SLM046 (tolerant) genotype, the expression levels of PYS, NCED, AAO3, and GR genes were increased after 8 h of foliar application. The expression level of the NTR gene was increased 8 and 24 h after stress and methanol treatment. In the Hyola308 genotype, PYS, AAO3, NTR, and GR genes' expression level was increased 8 h after methanol foliar application, and the NCED gene was increased 24 h after stress with methanol treatment. In general, methanol foliar application increased the expression levels of several genes. Particularly, the gene expression was considerably higher in the SLM046 genotype than in Hyola308. Bioinformatics prediction of microRNAs targeting PSY, NCED, GR, NTRC, and AAO3 genes was performed, and 38, 38, 13, 11, and 11 microRNAs were predicted for these genes, respectively. The study of effective microRNAs showed that sometimes more than one type of microRNA could affect the desired gene, and in some cases, a conserved family of microRNAs caused the main effect on gene expression. Overall, our results lay the foundation for functional characterization of these genes or gene-miRNA modules in regulating drought stress tolerance in rapeseed.
Keywords: Carotenoids; Gene expression; Protein interaction; STRING; microRNA.
© King Abdulaziz City for Science and Technology 2022, Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Ali S, Hayat K, Iqbal A, Xie L. Implications of abscisic acid in the drought stress tolerance of plants. Agronomy. 2020;10:1323. doi: 10.3390/agronomy10091323. - DOI
-
- Aono M, Kubo A, Saji H, Tanaka K, Kondo N. Enhanced tolerance to photooxidative stress of transgenic Nicotiana tabacum with high chloroplastic glutathione reductase activity. Plant Cell Physiol. 1993;34:129–135. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.pcp.a078386. - DOI
-
- Armand N, Amiri H, Ismaili A. The effect of methanol on photosynthetic parameters of bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) under water deficit. Photosynthetica. 2016;54:288–294. doi: 10.1007/s11099-015-0178-2. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

