DCNN-FuzzyWOA: Artificial Intelligence Solution for Automatic Detection of COVID-19 Using X-Ray Images
- PMID: 35965746
- PMCID: PMC9363937
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/5677961
DCNN-FuzzyWOA: Artificial Intelligence Solution for Automatic Detection of COVID-19 Using X-Ray Images
Abstract
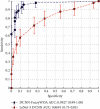
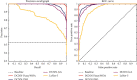
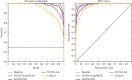
Artificial intelligence (AI) techniques have been considered effective technologies in diagnosing and breaking the transmission chain of COVID-19 disease. Recent research uses the deep convolution neural network (DCNN) as the discoverer or classifier of COVID-19 X-ray images. The most challenging part of neural networks is the subject of their training. Descent-based (GDB) algorithms have long been used to train fullymconnected layer (FCL) at DCNN. Despite the ability of GDBs to run and converge quickly in some applications, their disadvantage is the manual adjustment of many parameters. Therefore, it is not easy to parallelize them with graphics processing units (GPUs). Therefore, in this paper, the whale optimization algorithm (WOA) evolved by a fuzzy system called FuzzyWOA is proposed for DCNN training. With accurate and appropriate tuning of WOA's control parameters, the fuzzy system defines the boundary between the exploration and extraction phases in the search space. It causes the development and upgrade of WOA. To evaluate the performance and capability of the proposed DCNN-FuzzyWOA model, a publicly available database called COVID-Xray-5k is used. DCNN-PSO, DCNN-GA, and LeNet-5 benchmark models are used for fair comparisons. Comparative parameters include accuracy, processing time, standard deviation (STD), curves of ROC and precision-recall, and F1-Score. The results showed that the FuzzyWOA training algorithm with 20 epochs was able to achieve 100% accuracy, at a processing time of 880.44 s with an F1-Score equal to 100%. Structurally, the i-6c-2s-12c-2s model achieved better results than the i-8c-2s-16c-2s model. However, the results of using FuzzyWOA for both models have been very encouraging compared to particle swarm optimization, genetic algorithm, and LeNet-5 methods.
Copyright © 2022 Abbas Saffari et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- First T. Handbook of COVID-19 Prevention and Treatment
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

