Effects of 4-DAMP on allergic rhinitis in guinea pigs and its potential mechanism
- PMID: 35965822
- PMCID: PMC9372692
- DOI: 10.21037/atm-22-2998
Effects of 4-DAMP on allergic rhinitis in guinea pigs and its potential mechanism
Abstract
Background: Allergic rhinitis (AR) is a non-infectious chronic inflammatory disease of the nasal mucosa mainly mediated by immunoglobulin E (IgE), which seriously affects the life quality of affected patients. This study aimed to observe the effects of 1,1-dimethyl-4-diphenylacetoxypiperidinium iodide (4-DAMP; a selective M3 receptor antagonist) on ovalbumin (OVA)-induced AR guinea pigs, and to explore its potential mechanism of involvement.
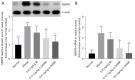
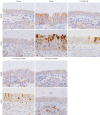
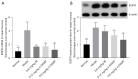
Methods: An AR model was established by inducing male guinea pigs (4-6 weeks of age) with OVA. AR guinea pigs were randomly divided into a model group, 0.6 mg/kg ipratropium bromide (IB) group, 0.12 and 0.6 mg/kg 4-DAMP group (n=18). The 0.6 mg/kg IB group, 0.12 and 0.6 mg/kg 4-DAMP group animals were treated with IB (0.6 mg/kg) and 4-DAMP (0.12 or 0.6 mg/kg) by intranasal instillation per nostril daily. Animals in the model group and normal group were treated with saline as control. The AR symptom scores were counted and nasal secretion weights were measured. Histopathological methods were used to observe nasal mucosa. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) was used to detect the levels of histamine and cytokines. Western blot and quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) were used to detect the expressions of mucin 5AC (MUC5AC), matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP9), and epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR).
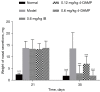
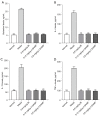
Results: Compared with model group animals, the AR symptom scores and nasal secretion weights of animals treated with 4-DAMP were reduced significantly, goblet cell metaplasia was reversed, and eosinophil infiltration was visibly alleviated. The levels of histamine and cytokines in nasal lavage fluid (NLF) were decreased, and the protein and messenger RNA (mRNA) expressions of MUC5AC, MMP9, and EGFR were inhibited.
Conclusions: Treatment with 4-DAMP has a certain effect on AR, especially for mucus hypersecretion, which provides a new idea for clinical treatment of AR.
Keywords: 1,1-dimethyl-4-diphenylacetoxypiperidinium iodide (4-DAMP); M3 receptor; allergic rhinitis (AR); chronic inflammatory; hypersecretion.
2022 Annals of Translational Medicine. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://atm.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/atm-22-2998/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Antagonism of m3 Alleviates Type 2 Inflammation in Allergic Rhinitis Mice.Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2023 May;37(3):264-272. doi: 10.1177/19458924221137977. Epub 2022 Nov 7. Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2023. PMID: 36343939
-
Gleditsia sinensis Lam. aqueous extract attenuates nasal inflammation in allergic rhinitis by inhibiting MUC5AC production through suppression of the STAT3/STAT6 pathway.Biomed Pharmacother. 2023 May;161:114482. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.114482. Epub 2023 Mar 13. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023. PMID: 36921533
-
Therapeutic potential of combined anti-IL-1β IgY and anti-TNF-α IgY in guinea pigs with allergic rhinitis induced by ovalbumin.Int Immunopharmacol. 2015 Mar;25(1):155-61. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2014.12.002. Epub 2014 Dec 11. Int Immunopharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25497231
-
Bencycloquidium bromide inhibits nasal hypersecretion in a rat model of allergic rhinitis.Inflamm Res. 2015 Apr;64(3-4):213-23. doi: 10.1007/s00011-015-0800-6. Epub 2015 Feb 18. Inflamm Res. 2015. PMID: 25690567
-
Ameliorative potential of galangin in murine model of ovalbumin-induced allergic rhinitis: a role of PI3K-PKB pathway.Am J Vet Res. 2024 May 6;85(6):ajvr.24.02.0031. doi: 10.2460/ajvr.24.02.0031. Print 2024 Jun 1. Am J Vet Res. 2024. PMID: 38697189
References
-
- Wang CS, Wang XD, Zhang L. An introduction to Allergic Rhinitis and its Impact on Asthma (ARIA) guidelines-2016 revision. Zhonghua Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi 2018;53:798-800. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
