Research progress on the mechanism of action of hesperetin in cerebral ischemia: a narrative review
- PMID: 35965833
- PMCID: PMC9372698
- DOI: 10.21037/atm-22-3136
Research progress on the mechanism of action of hesperetin in cerebral ischemia: a narrative review
Abstract
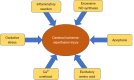
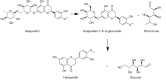
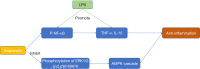
Background and objective: Ischemic cerebrovascular disease is one of the main diseases threatening human health and survival and is a commonly occurring disease in neurology. Due to its high disability rate, ischemic cerebrovascular disease is one of the most important diseases to be prevented and treated at present. The risk factors of cerebral ischemia include atherosclerosis, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and blood viscosity caused by thrombocytosis. After cerebral ischemia, cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury may be induced by oxidative stress (OS), inflammatory reaction, nitric oxide damage, apoptosis, excitatory amino acid toxicity, calcium (Ca2+) overload, and other mechanisms. Hesperidin is a flavanone compound and is a key component in citrus plants. It is a kind of traditional Chinese medicine extract with high levels of Pericarpium, shell, fruit, and green peel. In recent years, Hesperidin has received great attention, compelling evidence has indicated Hesperidin plays a beneficial role in cerebral ischemia.
Methods: We conducted a literature search for published manuscripts hesperidin in ischemia/reperfusion up to December 2021 in common English databases (i.e., PubMed, EMBASE, Web of Science, SpringerLink, Wiley, Cochrane Library) and Chinese databases [Chinese BioMedical Literature Service System (CBM), WANFANG database, China Knowledge Resource Integrated Database (CNKI)].
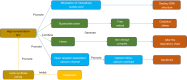
Key content and findings: In this article, we reviewed the mechanisms of action of hesperidin in the treatment of cerebral ischemia, including antioxidant stress, anti-inflammatory reaction, anti-atherosclerosis, anti-thrombosis, anti-apoptosis, and nitric oxide regulation.
Conclusions: In this narrative review, Hesperidin exhibits antioxidant stress, anti-platelet aggregation, vasodilation, anti-atherosclerotic, anti-inflammatory, anti-apoptotic, hypolipidemic, anti-tumor, cardiovascular protection, and nitric oxide-release regulatory properties Such a comprehension of the recent progress of hesperidin will help identify biomarkers for diagnosis and therapeutic targets to cerebral ischemia.
Keywords: Hesperetin; apoptosis; atherosclerosis; cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury; oxidative stress (OS).
2022 Annals of Translational Medicine. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://atm.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/atm-22-3136/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures




References
-
- Xie YP, Li YJ. Research progress on the risk factors of ischemic stroke. Chinese Journal of Integrative Medicine on Cardio-Cerebrovascular Disease 2019;17:1493-5.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
