Effect of Different Ankle-Foot Immobility on Lateral Gait Stability in the Stance Phase
- PMID: 35965839
- PMCID: PMC9365579
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/7135040
Effect of Different Ankle-Foot Immobility on Lateral Gait Stability in the Stance Phase
Abstract
Background: This study aimed to investigate the effect of limited foot and ankle mobility on the lateral stability of gait through the observation of the mediolateral margin of stability and related kinematic parameters.
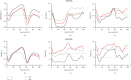
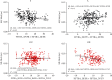
Methods: Thirty young, healthy participants walked at a fixed gait velocity on a level surface. Participants achieved different degrees of restricted mobility by wearing soft-soled shoes (S), an ankle-foot orthosis with unrestricted dorsiflexion-plantarflexion activity only (A), and an ankle-foot orthosis with unrestricted dorsiflexion-plantarflexion and adjustable horizontal rotation of the foot (OU/OR). Furthermore, the spatiotemporal parameters, mediolateral margin of stability, center of pressure, angle of the fore and hind foot relative to the tibia, and correlation coefficients of the factors were analyzed. Regression analysis was also performed.
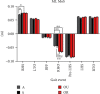
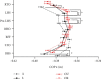
Results: At right heel strike, group A had a significantly lower mediolateral margin of stability than group S and group OU. Meanwhile, forefoot adduction (0.2 < |r| <0.4) and plantarflexion (0.2 < |r| <0.4), as well as hindfoot internal rotation (0.2 < |r| <0.6) and inversion (0.2 < |r| <0.4), correlated negatively with lateral stability. Regression analysis revealed forefoot dorsiflexion and supination were the main independent variables for group A. At right heel off, groups OU and OR had a significantly lower mediolateral margin of stability than those in groups A and S. Forefoot adduction (0.2 < |r| <0.4) and dorsiflexion (0.4 < |r| <0.6) were correlated with lateral stability, as were hindfoot dorsiflexion (0.2 < |r| <0.4) and inversion (0.2 < |r| <0.4). Regression analysis revealed forefoot abduction and plantarflexion were the main independent variables for groups OU and OR.
Conclusions: The present study verified from gait data that forefoot dorsiflexion and supination at the initial contact of the stance phase were relevant factors for the differences in lateral gait stability, whereas abduction and plantar flexion of the forefoot at the terminal stance phase were the main influencing factors of lateral gait stability.
Copyright © 2022 Wen Fan and Yasuhiko Hatanaka.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures



Similar articles
-
An Ankle-Foot Orthosis With a Lateral Extension Reduces Forefoot Abduction in Subjects With Stage II Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction.J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2016 Jan;46(1):26-33. doi: 10.2519/jospt.2016.5618. Epub 2015 Dec 11. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2016. PMID: 26654572 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of an articulated ankle-foot orthosis with resistance-adjustable joints on lower limb joint kinematics and kinetics during gait in individuals post-stroke.Clin Biomech (Bristol). 2018 Nov;59:47-55. doi: 10.1016/j.clinbiomech.2018.08.003. Epub 2018 Aug 10. Clin Biomech (Bristol). 2018. PMID: 30145413 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of a dynamic-ankle-foot orthosis (Liberté®) on kinematics and electromyographic activity during gait in hemiplegic patients with spastic foot equinus.NeuroRehabilitation. 2014;35(3):369-79. doi: 10.3233/NRE-141128. NeuroRehabilitation. 2014. PMID: 25227539
-
Contributions to the understanding of gait control.Dan Med J. 2014 Apr;61(4):B4823. Dan Med J. 2014. PMID: 24814597 Review.
-
Recurvatum of the Knee in Cerebral Palsy: A Review.Cureus. 2021 Apr 10;13(4):e14408. doi: 10.7759/cureus.14408. Cureus. 2021. PMID: 33859920 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

