Enucleation versus hepatectomy for hepatic hemangiomas: A meta-analysis
- PMID: 35965862
- PMCID: PMC9366102
- DOI: 10.3389/fsurg.2022.960768
Enucleation versus hepatectomy for hepatic hemangiomas: A meta-analysis
Abstract
Objective: To compare the safety and efficacy of enucleation and hepatectomy for the treatment of hepatic hemangioma (HH).
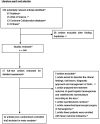
Methods: A systematic literature search was conducted to identify studies evaluating enucleation versus hepatectomy for HH starting from the time of database creation to February 2022. Extraction of the data used in this study was done from the literature. The differences between the two surgical approaches were evaluated by comparing and analyzing the relevant data by means of meta-analysis.
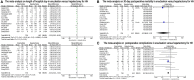
Results: A total of 1,384 patients (726 underwent enucleation, and 658 with hepatectomy) were included in our meta-analysis from 12 studies. Enucleations were associated with favorable outcomes in terms of operation time [mean difference (MD): -39.76, 95% confidence interval (CI): -46.23, -33.30], blood loss (MD: -300.42, 95% CI: -385.64, -215.19), length of hospital stay (MD: -2.33, 95% CI: -3.22, -1.44), and postoperative complications (OR: 0.57, 95% CI: 0.44-0.74). There were no differences between the groups in terms of patients needing transfusion (OR: 0.85, 95% CI: 0.50, 1.42), inflow occlusion time (MD: 1.72, 95% CI: -0.27, 3.71), and 30-day postoperative mortality (OR: 0.23, 95% CI: 0.02-2.17).
Conclusion: Compared with hepatectomy, enucleation is found to be effective at reducing postoperative complications, blood loss, and operation time and shortening the length of hospital stay. Enucleation is similar to hepatectomy in terms of inflow occlusion time, 30-day postoperative mortality, and patients needing transfusing to hepatectomy.
Keywords: enucleation; hepatectomy; hepatic hemangiomas; meta-analysis; treatment.
© 2022 Jiang, Shen, Fang and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Enucleation versus hepatectomy for giant hepatic haemangiomas: a meta-analysis.Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2017 Mar;99(3):237-241. doi: 10.1308/rcsann.2016.0349. Epub 2016 Nov 21. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2017. PMID: 27869486 Free PMC article.
-
Enucleation of liver hemangiomas: is there a difference in surgical outcomes for centrally or peripherally located lesions?Am J Surg. 2009 Aug;198(2):184-7. doi: 10.1016/j.amjsurg.2008.09.029. Epub 2009 Mar 25. Am J Surg. 2009. PMID: 19324327
-
Enucleation versus Anatomic Resection for Giant Hepatic Hemangioma: A Meta-Analysis.Gastrointest Tumors. 2017 Mar;3(3-4):153-162. doi: 10.1159/000455846. Epub 2017 Feb 11. Gastrointest Tumors. 2017. PMID: 28611982 Free PMC article.
-
Safety and efficacy for laparoscopic versus open hepatectomy: A meta-analysis.Surg Oncol. 2018 Jun;27(2):A26-A34. doi: 10.1016/j.suronc.2017.06.007. Epub 2017 Jun 28. Surg Oncol. 2018. PMID: 28687154 Review.
-
Laparoscopic versus Robotic Hepatectomy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Clin Med. 2022 Sep 30;11(19):5831. doi: 10.3390/jcm11195831. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 36233697 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Management of Neonatal Hepatic Hemangiomas: A Single-Center Experience Focused on Challenging Cases.J Clin Med. 2024 May 11;13(10):2839. doi: 10.3390/jcm13102839. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 38792380 Free PMC article.
-
Laparoscopic liver resection or enucleation for giant hepatic hemangioma: how to choose?Surg Endosc. 2024 Jun;38(6):3079-3087. doi: 10.1007/s00464-024-10820-z. Epub 2024 Apr 15. Surg Endosc. 2024. PMID: 38622227
References
-
- Demircan O, Demiryurek H, Yagmur O. Surgical approach to symptomatic giant cavernous hemangioma of the liver. Hepatogastroenterology. (2005) 52:183–6. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources