Kyphoplasty for thoracic and lumbar fractures with an intravertebral vacuum phenomenon in ankylosing spondylitis patients
- PMID: 35965876
- PMCID: PMC9372763
- DOI: 10.3389/fsurg.2022.962723
Kyphoplasty for thoracic and lumbar fractures with an intravertebral vacuum phenomenon in ankylosing spondylitis patients
Abstract
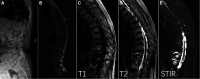
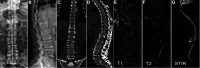
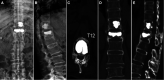
Background: Intravertebral vacuum phenomenon (IVP) is a special sign after vertebral fractures, which is common in patients with ankylosing spondylitis (AS) and may indicate pseudarthrosis and bone nonunion that lead to spinal instability. The objective of this study is to evaluate the efficacy and safety of kyphoplasty (KP) in treating such types of vertebral fractures with AS.
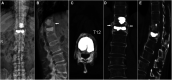
Methods: Sixteen patients with AS suffering from thoracic or lumbar fractures with IVP received KP from 2015 to 2020 and were monitored for more than 1 year. The visual analog scale (VAS) score was used to evaluate back pain relief. The Oswestry Disability Index (ODI) questionnaire was used to assess the improvement of the patients' living quality. The anterior and middle vertebral height restoration ratio (AVH, MVH) and the kyphotic angle (KA) were used to evaluate the radiographic results.
Results: The mean follow-up period was 20.8 months (12-28 months). The VAS and ODI significantly reduced at 3 days, 3 months after surgery, and at the last follow-up compared with the preoperative outcomes (p < 0.05). The AVH and MVH were significantly increased compared with the preoperative outcomes (p < 0.05). There was a significant correction in the KA between pre- and postoperative assessments (p < 0.05). Asymptomatic intradiscal polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA) cement leakage was found in two patients.
Conclusions: For thoracic or lumbar fractures with IVP in AS patients, KP may be safe and effective, which achieves pain relief and satisfying functional improvement, restores the anterior and middle height, and corrects the kyphotic angle of the fractured vertebra.
Keywords: PMMA; ankylosing spondylitis; intravertebral vacuum phenomenon; kyphoplasty; vertebral fracture.
© 2022 Liu, Zhou, Zhang, Deng, Hu, He, Liu and Yang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

