Global Trends of Sunscreen Research Literature: A Bibliometric Analysis over the Period of 2010-2020
- PMID: 35965897
- PMCID: PMC9364452
- DOI: 10.4103/JCAS.JCAS_110_21
Global Trends of Sunscreen Research Literature: A Bibliometric Analysis over the Period of 2010-2020
Abstract
Objective: To date, little effort has been devoted to summarizing worldwide research trends in sunscreen publications. The present study aimed to quantitatively analyze research trends in sunscreen publications over the past period from 2010 to 2020.
Materials and methods: The required bibliometric information was extracted and downloaded from the Scopus database. Documents including the keywords "Sunscreen" and "Sunscreens" were extracted from the database. A total of 1466 articles were retrieved from the database as on May 14, 2021. Data analysis and visualization were performed through RStudio. The bibliometrix package was accessed through the RStudio application to compute and process the bibliotec file.
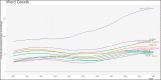
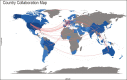
Results: Over the last decade (2010-2020), marked progress has been made in the area of sunscreens research. The overall increase in publications and citations reflects a growing research interest in the sunscreens field. The United States was the most prolific organization productive country with (n = 861) published documents, followed by Brazil (n = 273), Australia (n = 220), and France (n = 220). The most active institution was the Universidade Federal do Rio de Janeiro with publications (n = 30). Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology was the leading journal in the sunscreen literature with a total of (n = 55) documents.
Conclusion: The main strength of the study is the use of the bibliometric analysis method and visualization of data to review the entire literature on sunscreens. The United States, Brazil, the United Kingdom, Australia, France, and China were active in most of the research parameters included in the study. These findings serve as a guide and road map for scholars in the field. This research can also be beneficial to academics, policymakers, and educational use.
Keywords: Bibliometric; global; sunscreen.
Copyright: © 2022 Journal of Cutaneous and Aesthetic Surgery.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Moloney FJ, Collins S, Murphy GM. Sunscreens: safety, efficacy and appropriate use. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2002;3:185–91. - PubMed
-
- Forecasted market value of sunscreen cream worldwide in 2019 and 2024. Available at: https://www.statista.com/statistics/866356/sunscreen-ingredients-global-... Accessed on 2 October 2021.
-
- Mohiuddin AK. Sunscreen and suntan preparations. ARC Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences (AJPS) 2019;5:8–44.
-
- Bens G. Sunscreens. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2014;810:429–63. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous