Microdroplet Botulinum Toxin: A Review
- PMID: 35965899
- PMCID: PMC9364467
- DOI: 10.4103/JCAS.JCAS_162_21
Microdroplet Botulinum Toxin: A Review
Abstract
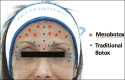
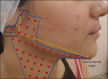
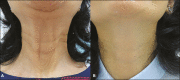
Microbotox is the administration of multiple microdroplets of botulinum toxin in intradermal plane. It is increasingly becoming popular owing to its more favorable outcome and better safety profile than the conventional technique. The intention is to treat fine lines and wrinkles without imparting an undesired "frozen face like" appearance. Besides facial rejuvenation, it has found its way into the management of other indications such as rosacea, hyperhidrosis, keloid, and seborrhea. Being a relatively newer method, knowledge about the various dilution methods, desired volume, and correct depth of injection involved in this technique remain scarce. In this article, the authors have highlighted various indications, procedures, adverse effects, and contraindications of microbotox.
Keywords: Botulinum toxin; facelift; facial wrinkles; mesobotox; microbotox; microdroplet technique.
Copyright: © 2022 Journal of Cutaneous and Aesthetic Surgery.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Wu WTL. Microbotox of the lower face and neck: Evolution of a personal technique and its clinical effects. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2015;136:92S–100S. - PubMed
-
- Wu WTL. Regional Conference in Dermotological Laser and Facial Cosmetic Surgery 2002: Hong Kong; 2002. Facial rejuvenation without facelifts – personal strategies.
-
- Sapra P, Demay S, Sapra S, Khanna J, Mraud K, Bonadonna J. A single-blind, split-face, randomized, pilot study comparing the effects of intradermal and intramuscular injection of two commercially available botulinum toxin A formulas to reduce signs of facial aging. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2017;10:34–44. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rose AE, Goldberg DJ. Safety and efficacy of intradermal injection of botulinum toxin for the treatment of oily skin. Dermatol Surg. 2013;39:443–8. - PubMed
-
- Trindade de Almeida AR, Marques E, de Almeida J, de Almeida J, Cunha T, Boraso R. Pilot study comparing the diffusion of two formulations of botulinum toxin type A in patients with forehead hyperhidrosis. Dermatol Surg. 2007;33:S37–43. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
