Proteomic profiling of thyroid tissue in patients with obesity and benign diffuse goiter
- PMID: 35966064
- PMCID: PMC9365950
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2022.923465
Proteomic profiling of thyroid tissue in patients with obesity and benign diffuse goiter
Abstract
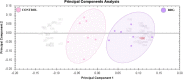
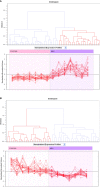
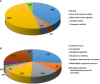
Goiter is a term to describe the enlargement of the thyroid gland. The pathophysiology and molecular changes behind development of diffuse benign goiter remains unclear. The present study targeted to identify and describe the alterations in the thyroid tissue proteome from patients (obese euthyroid) with benign diffuse goiter (BDG) using proteomics approach. Thyroid tissue samples, from 7 age and sex matched, patients with BDG and 7 controls were obtained at the time of surgery. An untargeted proteomic analysis of the thyroid tissue was performed out utilizing two-dimensional difference (2D-DIGE) in gel electrophoresis followed by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF-MS) for identification of the proteins. Progenesis software was used to identify changes in expression of tissue proteins and found statistically significant differences in abundance in a total of 90 proteins, 46 up and 44 down (1.5-fold change, ANOVA, p ≤ 0.05) in BDG compared to the control group. Bioinformatic analysis using Ingenuity Pathway Analysis (IPA) identified dysregulation of signalling pathways linked to ERK1/2, Glutathione peroxidase and NADPH oxidase associated to organismal injury and abnormalities, endocrine system disorders and cancer. The thyroid tissue proteome in patients with BDG revealed a significant decrease in thyroglobulin along with dysregulation of glycolysis and an increase in prooxidant peroxidase enzymes. Dysregulation of metabolic pathways related to glycolysis, redox proteins, and the proteins associated with maintaining the cytoskeletal structure of the thyrocytes was also identified.
Keywords: 2D-DIGE; MALDI-TOF; goiter; obese; proteomics; thyroid tissue.
Copyright © 2022 Benabdelkamel, Rafiullah, Masood, Alsaif, Musambil and Alfadda.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be considered as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Identification of Protein Changes in the Urine of Hypothyroid Patients Treated with Thyroxine Using Proteomics Approach.ACS Omega. 2021 Jan 13;6(3):2367-2378. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.0c05686. eCollection 2021 Jan 26. ACS Omega. 2021. PMID: 33521475 Free PMC article.
-
A matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization imaging mass spectrometric approach to study weight-related changes within thyroid tissue.J Mass Spectrom. 2021 Jan;56(1):e4671. doi: 10.1002/jms.4671. Epub 2020 Nov 10. J Mass Spectrom. 2021. PMID: 33169897
-
Proteomics Profiling of the Urine of Patients with Hyperthyroidism after Anti-Thyroid Treatment.Molecules. 2021 Apr 1;26(7):1991. doi: 10.3390/molecules26071991. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33915895 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma-Based Proteomics Profiling of Patients with Hyperthyroidism after Antithyroid Treatment.Molecules. 2020 Jun 19;25(12):2831. doi: 10.3390/molecules25122831. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32575434 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
[Advances in plant proteomics--I. Key techniques of proteome].Yi Chuan. 2006 Nov;28(11):1472-86. doi: 10.1360/yc-006-1472. Yi Chuan. 2006. PMID: 17098721 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Proteomics Investigation of the Impact of the Enterococcus faecalis Secretome on MCF-7 Tumor Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 5;24(19):14937. doi: 10.3390/ijms241914937. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37834385 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Blanc E, Ponce C, Brodschi D, Nepote A, Barreto A, Schnitman M, et al. . Association between worse metabolic control and increased thyroid volume and nodular disease in elderly adults with metabolic syndrome. Metab Syndrome Related Disord (2015) 13(5):221–6. doi: 10.1089/met.2014.0158 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

