Movement characteristics during customized exergames after total knee replacement in older adults
- PMID: 35966111
- PMCID: PMC9363837
- DOI: 10.3389/fspor.2022.915210
Movement characteristics during customized exergames after total knee replacement in older adults
Abstract
Introduction: There is limited understanding of how older adults can reach kinematic goals in rehabilitation while performing exergames and conventional exercises, and how similar or different the kinematics during exergaming are when compared with conventional therapeutic exercise with similar movement. The aim of this study was to describe the movement characteristics performed during exercise in custom-designed exergames and conventional therapeutic exercises among patients who have undergone unilateral total knee replacement (TKR). In addition, the secondary aim was to assess the relation of these exercise methods, and to assess participants' perceived exertion and knee pain during exergaming and exercising.
Materials and methods: Patients up to 4 months after the TKR surgery were invited in a single-visit exercise laboratory session. A 2D motion analysis and force plates were employed to evaluate movement characteristics as the volume, range, and intensity of movement performed during custom-designed knee extension-flexion and weight shifting exergames and conventional therapeutic exercises post TKR. The perceived exertion and knee pain were assessed using the Borg Rating of Perceived Exertion and Visual Analog Scale, respectively.
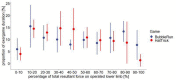
Results: Evaluation of seven patients with TKR [age median (IQR), 65 (10) years] revealed that the volume and intensity of movement were mostly higher during exergames. Individual goniometer-measured knee range of motion were achieved either with exergames and conventional therapeutic exercises, especially in knee extension exercises. The perceived exertion and knee pain were similar after exergames and conventional therapeutic exercises.
Conclusions: During custom-designed exergaming the patients with TKR achieve the movement characteristics appropriate for post-TKR rehabilitation without increasing the stress and pain experienced even though the movement characteristics might be partly different from conventional therapeutic exercises by the volume and intensity of movement. Physical therapists could consider implementing such exergames in rehabilitation practice for patients with TKR once effectiveness have been approved and they are widely available.
Keywords: exercise therapy; kinematics; musculoskeletal system; physical therapy; rehabilitation; video games.
Copyright © 2022 Janhunen, Löppönen, Walker, Punsár, Katajapuu, Cheng, Paloneva, Pamilo, Luimula, Korpelainen, Jämsä, Heinonen and Aartolahti.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Aartolahti E., Janhunen M., Katajapuu N., Paloneva J., Pamilo K., Keemu H., et al. . (2022). Effectiveness of gamification in knee replacement rehabilitation: protocol for a randomized controlled trial (BEE-RCT) with a qualitative approach. JMIR Prepr. 38434. 10.2196/preprints.38434 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Beswick A. D., Wylde V., Gooberman-Hill R., Blom A., Dieppe P. (2012). What proportion of patients report long-term pain after total hip or knee replacement for osteoarthritis? A systematic review of Prospective studies in unselected patients. BMJ Open 2, 1–12. 10.1136/bmjopen-2011-000435 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bruyère O., Honvo G., Veronese N., Arden N. K., Branco J., Curtis E. M., et al. . (2019). An updated algorithm recommendation for the management of knee osteoarthritis from the European Society for Clinical and Economic Aspects of Osteoporosis, Osteoarthritis and Musculoskeletal Diseases (ESCEO). Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 49, 337–350. 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2019.04.008 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

