Recent Progress Toward Imaging Application of Multifunction Sonosensitizers in Sonodynamic Therapy
- PMID: 35966148
- PMCID: PMC9365495
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S370767
Recent Progress Toward Imaging Application of Multifunction Sonosensitizers in Sonodynamic Therapy
Abstract
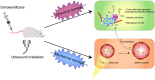
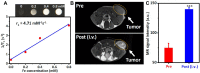
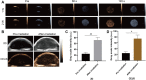
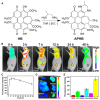
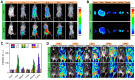
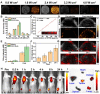
Sonodynamic therapy (SDT) is a rapidly developing non-surgical therapy that initiates sensitizers' catalytic reaction using ultrasound, showing great potential for cancer treatment due to its high safety and non-invasive nature. In addition, recent research has found that using different diagnostic and therapeutic methods in tandem can lead to better anticancer outcomes. Therefore, as essential components of SDT, sonosensitizers have been extensively explored to optimize their functions and integrate multiple medical fields. The review is based on five years of articles evaluating the combined use of SDT and imaging in treating cancer. By developing multifunctional sonosensitive particles that combine imaging and sonodynamic therapy, we have integrated diagnosis into the treatment of precision medicine applications, improving SDT cell uptake and antitumor efficacy utilizing different tumour models. This paper describes the imaging principle and the results of cellular and animal imaging of the multifunctional sonosensitizers. Efforts are made in this paper to provide data and design references for future SDT combined imaging research and clinical application development and to provide offer suggestions.
Keywords: imaging; multifunctional sonosensitizers; sonodynamic therapy; ultrasound.
© 2022 Wang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Ultrasound-Activated Sensitizers and Applications.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2020 Aug 17;59(34):14212-14233. doi: 10.1002/anie.201906823. Epub 2020 May 11. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2020. PMID: 31267634 Review.
-
Organic Sonosensitizers for Sonodynamic Therapy: From Small Molecules and Nanoparticles toward Clinical Development.Small. 2021 Oct;17(42):e2101976. doi: 10.1002/smll.202101976. Epub 2021 Aug 4. Small. 2021. PMID: 34350690 Review.
-
Sonodynamic therapy (SDT): a novel strategy for cancer nanotheranostics.Sci China Life Sci. 2018 Apr;61(4):415-426. doi: 10.1007/s11427-017-9262-x. Epub 2018 Apr 2. Sci China Life Sci. 2018. PMID: 29666990 Review.
-
Sonosensitizers for Sonodynamic Therapy: Current Progress and Future Perspectives.Ultrasound Med Biol. 2025 May;51(5):727-734. doi: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2025.01.011. Epub 2025 Feb 5. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2025. PMID: 39909788 Review.
-
Design and Challenges of Sonodynamic Therapy System for Cancer Theranostics: From Equipment to Sensitizers.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2021 Mar 12;8(10):2002178. doi: 10.1002/advs.202002178. eCollection 2021 May. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2021. PMID: 34026428 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Engineering Fe/Mn-doped zinc oxide nanosonosensitizers for ultrasound-activated and multiple ferroptosis-augmented nanodynamic tumor suppression.Mater Today Bio. 2022 Oct 5;16:100452. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2022.100452. eCollection 2022 Dec. Mater Today Bio. 2022. PMID: 36245834 Free PMC article.
-
Application of biomechanics in tumor epigenetic research.Mechanobiol Med. 2024 Aug 22;2(4):100093. doi: 10.1016/j.mbm.2024.100093. eCollection 2024 Dec. Mechanobiol Med. 2024. PMID: 40395222 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sonodynamic therapy and magnetic resonance-guided focused ultrasound: new therapeutic strategy in glioblastoma.J Neurooncol. 2023 May;163(1):219-238. doi: 10.1007/s11060-023-04333-3. Epub 2023 May 14. J Neurooncol. 2023. PMID: 37179515 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Focused ultrasound as a treatment modality for gliomas.Front Neurol. 2024 May 15;15:1387986. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1387986. eCollection 2024. Front Neurol. 2024. PMID: 38813245 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multifunctional Phase-Transition Nanoparticles for Effective Targeted Sonodynamic-Gene Therapy Against Thyroid Papillary Carcinoma.Int J Nanomedicine. 2023 May 2;18:2275-2293. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S394504. eCollection 2023. Int J Nanomedicine. 2023. PMID: 37159806 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

