Increase in eosinophil-derived neurotoxin level in school children with allergic disease
- PMID: 35966157
- PMCID: PMC9353201
- DOI: 10.5415/apallergy.2022.12.e25
Increase in eosinophil-derived neurotoxin level in school children with allergic disease
Abstract
Background: Eosinophils are major effector cells of allergic disease and excellent markers of eosinophilic inflammation. Accurate and reliable biomarkers are helpful in the diagnosis, treatment, and control of allergic disease.
Objective: This study aimed to investigate an alternate marker of eosinophilic inflammation, eosinophil-derived neurotoxin (EDN), in a number of allergic diseases.
Methods: Three hundred ninety-six elementary school-age children with various allergic conditions were recruited for this study. Subgroups included food allergies (FAs), atopic dermatitis (AD), bronchial asthma (BA), and allergic rhinitis (AR). EDN levels in these groups were compared to those in 93 healthy controls (HC).
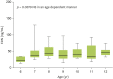
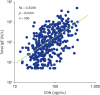
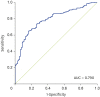
Results: All subjects with allergic disease had elevated levels of serum EDN (median [interquartile range]: FA, 124.2 ng/mL [59.13-160.5 ng/mL]; AD, 110.8 ng/mL [57.52-167.9 ng/mL]; BA, 131.5 ng/mL [60.60-171.0 ng/mL]; AR, 91.32 ng/mL [46.16-145.0 ng/mL]) compared to HC (38.38 ng/mL [32.40-55.62 ng/mL]) (p < 0.0001). These elevated levels were consistent throughout the age range (6-12 years) of the healthy study subjects (p = 0.0679). EDN levels also correlated well with total immunoglobulin E (Rs = 0.5599, p < 0.0001). Looking at all individuals with an allergic disease, the area under the curve was 0.790.
Conclusions: Direct measures of eosinophilic inflammation are needed for accurate diagnosis, treatment, and monitoring of allergic diseases. EDN may be a worthy biomarker of eosinophil activity and a useful screening tool for allergic diseases including FA, AD, BA, and AR.
Keywords: Allergic rhinitis; Atopic dermatitis; Biomarkers; Bronchial asthma; Eosinophil-derived neurotoxin; Food allergy.
Copyright © 2022. Asia Pacific Association of Allergy, Asthma and Clinical Immunology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Busse WW, Rosenwasser LJ. Mechanisms of asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2003;111:S799–S804. - PubMed
-
- Moqbel R, Lace P, Adamko DJ, Odemuyiwa SO. In: Allergy: principles & practice. Adkinson NF Jr, Bochner BS, Busse WW, Holgate ST, Lemanske JrRF, Simons FER, editors. St. Louis: Mosby; 2008. Biology of eosinophils; pp. 295–310.
-
- Gleich GJ, Adolphson CR. In: Interleukin-5: from molecule to drug target for asthma, (lung biology in health and disease) Sanderson CJ, editor. New York: Marcel Dekker; 1999. The eosinophil and bronchial asthma: evidence for a critical role of eosinophils in pathophysiology; pp. 1–37.
-
- Kim CK, Callaway Z, Park JS, Kwon EM. Utility of serum eosinophil-derived neurotoxin (EDN) measurement by ELISA in young children with asthma. Allergol Int. 2017;66:70–74. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
