A broad look into the future of systemic sclerosis
- PMID: 35966183
- PMCID: PMC9373175
- DOI: 10.1177/1759720X221109404
A broad look into the future of systemic sclerosis
Abstract
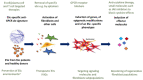
Systemic sclerosis (SSc) is a systemic autoimmune disease with the key features of inflammation, vasculopathy and fibrosis. This article focussed on emerging fields based on the authors' current work and expertise. The authors provide a hierarchical structure into the studies of the pathogenesis of SSc starting with the contribution of environmental factors. Regulatory autoantibodies (abs) are discussed, which are parts of the human physiology and are specifically dysregulated in SSc. Abs against the angiotensin II receptor subtype 1 (AT1R) and the endothelin receptor type A (ETAR) are discussed in more detail. Extracellular vesicles are another novel player to possess disease processes. Fibroblasts are a key effector cell in SSc. Therefore, the current review will provide an overview about their plasticity in the phenotype and function. Promising nuclear receptors as key regulators of transcriptional programmes will be introduced as well as epigenetic modifications, which are pivotal to maintain the profibrotic fibroblast phenotype independent of external stimuli. Fibroblasts from SSc patients exhibit a specific signalling and reactivate developmental pathways and stem cell maintenance such as by employing hedgehog and WNT, which promote fibroblast-to-myofibroblast transition and extracellular matrix generation. Pharmacological interventions, although for other indications, are already in clinical use to address pathologic signalling.
Keywords: autoantibodies; fibrosis; signalling; systemic sclerosis.
© The Author(s), 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Autoantibodies to angiotensin and endothelin receptors in systemic sclerosis induce cellular and systemic events associated with disease pathogenesis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2014 Jan 28;16(1):R29. doi: 10.1186/ar4457. Arthritis Res Ther. 2014. PMID: 24472528 Free PMC article.
-
When natural antibodies become pathogenic: autoantibodies targeted against G protein-coupled receptors in the pathogenesis of systemic sclerosis.Front Immunol. 2023 Jun 8;14:1213804. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1213804. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37359516 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vascular receptor autoantibodies in pulmonary arterial hypertension associated with systemic sclerosis.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2014 Oct 1;190(7):808-17. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201403-0442OC. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2014. PMID: 25181620
-
Angiotensin receptor type 1 and endothelin receptor type A on immune cells mediate migration and the expression of IL-8 and CCL18 when stimulated by autoantibodies from systemic sclerosis patients.Arthritis Res Ther. 2014 Mar 11;16(2):R65. doi: 10.1186/ar4503. Arthritis Res Ther. 2014. PMID: 24612997 Free PMC article.
-
Vascular hypothesis revisited: Role of stimulating antibodies against angiotensin and endothelin receptors in the pathogenesis of systemic sclerosis.Autoimmun Rev. 2016 Jul;15(7):690-4. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2016.03.005. Epub 2016 Mar 10. Autoimmun Rev. 2016. PMID: 26970493 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification and validation of anti-protein arginine methyltransferase 5 (PRMT5) antibody as a novel biomarker for systemic sclerosis (SSc).Ann Rheum Dis. 2024 Aug 27;83(9):1144-1155. doi: 10.1136/ard-2024-225596. Ann Rheum Dis. 2024. PMID: 38684324 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aguila LA, da Silva HC, Medeiros-Ribeiro AC, et al.. Is exposure to environmental factors associated with a characteristic clinical and laboratory profile in systemic sclerosis? A retrospective analysis. Rheumatol Int 2021; 41: 1143–1150. - PubMed
-
- Schmid M, Grolimund Berset D, Krief P, et al.. Should systemic sclerosis be recognised as an occupational disease in Switzerland? Swiss Med Wkly 2020; 150: w20193. - PubMed
-
- Cabral-Marques O, Riemekasten G. Functional autoantibodies targeting G protein-coupled receptors in rheumatic diseases. Nat Rev Rheumatol 2017; 13: 648–656. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

