The role of Cdk5 in neurological disorders
- PMID: 35966199
- PMCID: PMC9368323
- DOI: 10.3389/fncel.2022.951202
The role of Cdk5 in neurological disorders
Abstract
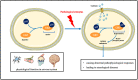
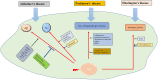
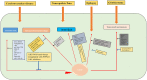
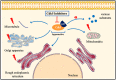
Neurological disorders are a group of disorders with motor, sensory or cognitive damage, caused by dysfunction of the central or peripheral nervous system. Cyclin-dependent kinases 5 (Cdk5) is of vital significance for the development of the nervous system, including the migration and differentiation of neurons, the formation of synapses, and axon regeneration. However, when the nervous system is subject to pathological stimulation, aberrant activation of Cdk5 will induce abnormal phosphorylation of a variety of substrates, resulting in a cascade signaling pathway, and thus lead to pathological changes. Cdk5 is intimately related to the pathological mechanism of a variety of neurological disorders, such as A-β protein formation in Alzheimer's disease, mitochondrial fragmentation in cerebral ischemia, and apoptosis of dopaminergic neurons in Parkinson's disease. It is worth noting that Cdk5 inhibitors have been reported to have neuroprotective effects by inhibiting related pathological processes. Therefore, in this review, we will briefly introduce the physiological and pathological mechanisms of Cdk5 in the nervous system, focusing on the recent advances of Cdk5 in neurological disorders and the prospect of targeted Cdk5 for the treatment of neurological disorders.
Keywords: CDK5 inhibitor; cyclin-dependent kinases 5 (Cdk5); nervous system; neurological disorders; therapeutic targets.
Copyright © 2022 Ao, Li, Chen, Tan, and Zeng.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ai J., Wang H., Chu P., Shopit A., Niu M., Ahmad N., et al. . (2022). The neuroprotective effects of phosphocreatine on amyloid beta 25-35-induced differentiated neuronal cell death through inhibition of AKT/GSK-3β/Tau/APP/CDK5 pathways in vivo and vitro. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 179, 416–417. 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2021.12.306 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Banerjee J., Srivastava A., Sharma D., Dey S., Tripathi M., Sharma M. C., et al. . (2021). Differential regulation of excitatory synaptic transmission in the hippocampus and anterior temporal lobe by cyclin dependent kinase 5 (Cdk5) in mesial temporal lobe epilepsy with hippocampal sclerosis (MTLE-HS). Neurosci. Lett. 761:136096. 10.1016/j.neulet.2021.136096 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

