Nasal Cytology: A Easy Diagnostic Tool in Precision Medicine for Inflammation in Epithelial Barrier Damage in the Nose. A Perspective Mini Review
- PMID: 35966227
- PMCID: PMC9365292
- DOI: 10.3389/falgy.2022.768408
Nasal Cytology: A Easy Diagnostic Tool in Precision Medicine for Inflammation in Epithelial Barrier Damage in the Nose. A Perspective Mini Review
Abstract
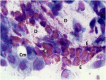
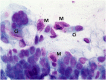
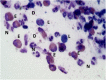
Nasal cytology is a diagnostic tool that can be used in precision rhinology medicine. Particularly in non-allergic rhinitis and chronic rhinosinusitis forms it can be useful to evaluate biomarkers of both surgical or biological therapy and especially in the follow-up it must be used to predict the prognostic index of recurrence of nasal polyposis. All inflammatory cytokines are also linked to the presence of cells such as eosinophils and mastcells and nasal cytology is a non-invasive and repeatable method to assess the situation in real life.
Keywords: NARES; biomarker; chronic rhinosinusitis; nasal cytology; non-allergic rhinitis; precision medicine.
Copyright © 2022 Caruso, Giancaspro, Guida, Macchi, Landi, Heffler and Gelardi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The pragmatic role of nasal cytology: a point-of-care testing to implement precision medicine in clinical practice.Rev Alerg Mex. 2018 Jul-Sep;65(3):259-263. doi: 10.29262/ram.v65i3.373. Rev Alerg Mex. 2018. PMID: 30176204 English.
-
Nasal cytology in children: recent advances.Ital J Pediatr. 2012 Sep 25;38:51. doi: 10.1186/1824-7288-38-51. Ital J Pediatr. 2012. PMID: 23009215 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Potential Role of Nasal Cytology in Respiratory Diseases: Clinical Research and Future Perspectives.J Clin Med. 2025 Jan 29;14(3):884. doi: 10.3390/jcm14030884. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 39941555 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In vitro diagnosis of chronic nasal inflammation.Clin Exp Allergy. 2004 Jul;34(7):1086-92. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.2004.01989.x. Clin Exp Allergy. 2004. PMID: 15248854
-
Focus on the Involvement of the Nose and Paranasal Sinuses in Eosinophilic Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis (Churg-Strauss Syndrome): Nasal Cytology Reveals Infiltration of Eosinophils as a Very Common Feature.Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2018;175(1-2):61-69. doi: 10.1159/000484602. Epub 2018 Jan 23. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29393242
Cited by
-
Nasal cytology and histology in CRSwNP: Two sides of the same coin.Front Med (Lausanne). 2023 Mar 9;10:1143351. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1143351. eCollection 2023. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 36968832 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison between clinical and cytological findings in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps treated with Dupilumab.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2024 Dec;281(12):6511-6521. doi: 10.1007/s00405-024-08958-6. Epub 2024 Sep 16. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2024. PMID: 39284942
-
Eosinophil-mast cell pattern of intraepithelial infiltration as a marker of severity in CRSwNP.Sci Rep. 2023 Jul 26;13(1):12101. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-39149-8. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37495667 Free PMC article.
-
Histopathological and Molecular Insights into Chronic Nasopharyngeal and Otic Disorders in Children: Structural and Immune Mechanisms Underlying Disease Chronicity.Life (Basel). 2025 Aug 3;15(8):1228. doi: 10.3390/life15081228. Life (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40868875 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nasal cytological evidence of chronic inflammation in the olfactory cleft in post-viral olfactory dysfunction.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2025 May;282(5):2389-2397. doi: 10.1007/s00405-025-09302-2. Epub 2025 Mar 26. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2025. PMID: 40140006 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gelardi M, Iannuzzi L, De Giosa M, Taliente S, De Candia N, Quaranta N, et al. . Non-surgical management of chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps based on clinical-cytological grading: a precision medicine-based approach. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital. (2017) 37:38–45. 10.14639/0392-100X-1417 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gelardi M, Cavaliere C, Jannuzzi L. Nasal cytology. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. (2018) 32:37–40. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

