Subcutaneous panniculitis-like T-cell lymphoma after COVID-19 vaccination
- PMID: 35966352
- PMCID: PMC9364717
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jdcr.2022.08.006
Subcutaneous panniculitis-like T-cell lymphoma after COVID-19 vaccination
Keywords: COVID-19 vaccine; HLH, hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis; PET-CT, positron emission tomography–computed tomography; SPTCL; SPTCL, subcutaneous panniculitis-like T-cell lymphoma; SUV, standardized uptake value; TCR, T-cell receptor; injection site reaction; subcutaneous panniculitis-like T-cell lymphoma; viral vector vaccine.
Conflict of interest statement
None disclosed.
Figures
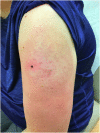
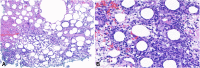
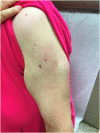
References
-
- Willemze R., Jansen P.M., Cerroni L., et al. Subcutaneous panniculitis-like T-cell lymphoma: definition, classification, and prognostic factors: an EORTC Cutaneous Lymphoma Group Study of 83 cases. Blood. 2008;111(2):838–845. - PubMed
-
- Parveen Z., Thompson K. Subcutaneous panniculitis-like T-cell lymphoma: redefinition of diagnostic criteria in the recent World Health Organization–European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer classification for cutaneous lymphomas. Arch Path Lab. 2009;133(2):303–308. - PubMed
-
- Abouyabis A.N., Shenoy P.J., Lechowicz M.J., Flowers C.R. Incidence and outcomes of the peripheral T-cell lymphoma subtypes in the United States. Leuk Lymphoma. 2008;49(11):2099–2107. - PubMed
-
- Trainor K.J., Brisco M.J., WanNeoh J.H., Grist S., Morley A.A. Gene rearrangement in B- and T-lymphoproliferative disease detected by the polymerase chain Reaction. Blood. 1991;78:192–196. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
