Expression, Clinical Significance, Immune Infiltration, and Regulation Network of miR-3940-5p in Lung Adenocarcinoma Based on Bioinformatic Analysis and Experimental Validation
- PMID: 35966511
- PMCID: PMC9365057
- DOI: 10.2147/IJGM.S375761
Expression, Clinical Significance, Immune Infiltration, and Regulation Network of miR-3940-5p in Lung Adenocarcinoma Based on Bioinformatic Analysis and Experimental Validation
Abstract
Background: Based on bioinformatics analysis and experimental validation, we investigated the expression, clinical significance, immune infiltration, and potential signaling pathways of miR-3940-5p in lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD).
Methods: 521 LUAD tissue samples and 46 normal lung tissue samples from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database. We evaluated the relationship between clinical features and miR-3940-5p expression using Kruskal-Wallis, Wilcoxon sign-rank, and logistic regression, explored the relationship between miR-3940-5p expression and the prognosis of LUAD patients using Kaplan-Meier survival curve analysis. Several databases were used to identify miRNA targets. MiR-3940-5p target genes were analyzed based on Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) analyses. The significant role of miR-3940-5p in function was evaluated using immune infiltration analysis. LUAD cell lines were tested for miR-3940-5p expression using QRT-PCR.
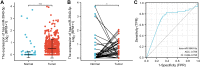
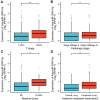
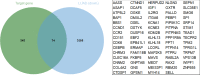
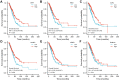
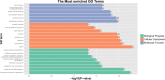
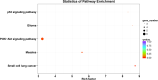
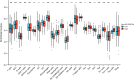
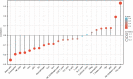
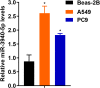
Results: There was a significant association between high miR-3940-5p expression in LUAD and T stage (P=0.005), pathologic stage (P=0.047), race (White vs Asian & Black or African American) (P=0.041), residual tumor (P=0.043), and anatomic neoplasm subdivision2 (P=0.030). MiR-3940-5p expression predicted poor overall survival (HR: 1.35; 95% CI: 1.01-1.81; P=0.045), disease-specific survival (HR: 1.53; 95% CI: 1.05-2.23; P=0.026), and progression-free survival (HR: 1.35; 95% CI: 1.03-1.77; P=0.032). BAP1, BBS1, CCR2, KCNE3, PEBP1, and RABL2A were all associated with poor OS in LUAD patients with low miR-3940-5p expression levels. According to GO and KEGG analyses, miR-3940-5p may play a role in LUAD development by regulating pathways such as measles, PI3K-Akt signaling pathway, and p53 signaling pathway. There was a correlation between the expression level of miR-3940-5p and immune infiltration. LUAD cell lines showed significantly higher levels of miR-3940-5p than Beas-2B cells.
Conclusion: A high expression of miR-3940-5p is significantly associated with a poor prognosis in patients with LUAD, suggesting that it could be used as a prognostic biomarker.
Keywords: clinical significance; immune infiltration; lung adenocarcinoma; microRNA-3940-5p; regulation network.
© 2022 Lin et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest relevant to this study.
Figures

Similar articles
-
MiR-195-3p is a Novel Prognostic Biomarker Associated with Immune Infiltrates of Lung Adenocarcinoma.Int J Gen Med. 2022 Jan 6;15:191-203. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S350340. eCollection 2022. Int J Gen Med. 2022. PMID: 35023957 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical value of microRNA-198-5p downregulation in lung adenocarcinoma and its potential pathways.Oncol Lett. 2019 Sep;18(3):2939-2954. doi: 10.3892/ol.2019.10610. Epub 2019 Jul 12. Oncol Lett. 2019. PMID: 31402959 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a novel prognosis-associated ceRNA network in lung adenocarcinoma via bioinformatics analysis.Biomed Eng Online. 2021 Nov 24;20(1):117. doi: 10.1186/s12938-021-00952-x. Biomed Eng Online. 2021. PMID: 34819106 Free PMC article.
-
Six MicroRNA Prognostic Models for Overall Survival of Lung Adenocarcinoma.Genet Res (Camb). 2022 Aug 27;2022:5955052. doi: 10.1155/2022/5955052. eCollection 2022. Genet Res (Camb). 2022. PMID: 36101742 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative Analysis of Three Novel Competing Endogenous RNA Biomarkers with a Prognostic Value in Lung Adenocarcinoma.Biomed Res Int. 2020 Aug 4;2020:2837906. doi: 10.1155/2020/2837906. eCollection 2020. Biomed Res Int. 2020. PMID: 32802839 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Unveiling the Enigmatic Role of SLC35F3 in Lung Adenocarcinoma.Clin Respir J. 2024 Oct;18(10):e70023. doi: 10.1111/crj.70023. Clin Respir J. 2024. PMID: 39414367 Free PMC article.
-
Development and Validation of a Prognostic Nomogram for Lung Adenocarcinoma: A Population-Based Study.J Healthc Eng. 2022 Dec 10;2022:5698582. doi: 10.1155/2022/5698582. eCollection 2022. J Healthc Eng. 2022. PMID: 36536690 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
High TLX1 Expression Correlates with Poor Prognosis and Immune Infiltrates in Patients with Lung Adenocarcinoma.Curr Mol Med. 2024;24(6):801-812. doi: 10.2174/1566524023666230619123752. Curr Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 37340746
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

